Liraglutide Attenuates Hepatic Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice by Modulating the Wnt/ β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 36756089
- PMCID: PMC9899592
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/8974960
Liraglutide Attenuates Hepatic Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice by Modulating the Wnt/ β-Catenin Signaling Pathway
Abstract
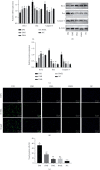
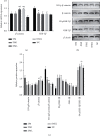
Liraglutide has been extensively applied in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus and also has hepatoprotective effects. However, the role of liraglutide treatment on liver injury in a mouse model of type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) induced by streptozotocin (STZ) and its underlying mechanisms remain to be elucidated. In the present study, diabetes was initiated in experimental animals by single-dose intraperitoneal inoculation of STZ. Forty female C57BL/6J mice were equally assigned into five groups: diabetic group, insulin+diabetic group, liraglutide+diabetic group, insulin+liraglutide+diabetic group, and control group for eight weeks. Diabetic mice exhibited a significantly elevated blood glucose level and decreased body weight, and morphological changes of increased steatosis and apoptosis were observed in the liver compared with the control. Furthermore, a significant increase in the levels of malondialdehyde and inflammatory markers such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and the proapoptotic proteins caspase-3 and Bax were observed in the livers of diabetic mice, together with marked increases in antioxidants superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX) as well as antiapoptotic protein Bcl-2, all of which were significantly mitigated by treatment with liraglutide, insulin, and their combinations. Interestingly, liraglutide monotherapy showed better efficacy in ameliorating liver injury in T1DM mice than insulin monotherapy, similar to the combined drug therapy. Furthermore, the expression of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway-associated molecules was upregulated in the liver of mice treated with liraglutide or insulin. The results of the present study suggested that liraglutide improves T1DM-induced liver injury and may have important implications for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in patients with T1DM.
Copyright © 2023 Jie Yu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- de Vries M., Westerink J., Kaasjager K., de Valk H. W. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism . 2020;105(12):3842–3853. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa575. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

