Systems and processes for regulation of investigational medical devices in Uganda
- PMID: 36756148
- PMCID: PMC9899893
- DOI: 10.3389/fmedt.2022.1054120
Systems and processes for regulation of investigational medical devices in Uganda
Abstract
Background: In many parts of the world, medical devices and the processes of their development are tightly regulated. However, the current regulatory landscape in Uganda like other developing countries is weak and poorly defined, which creates significant barriers to innovation, clinical evaluation, and translation of medical devices.
Aim: To evaluate current knowledge, systems and infrastructure for medical devices regulation and innovation in Uganda.
Methods: A mixed methods study design using the methods triangulation strategy was employed in this study. Data of equal weight were collected sequentially. First, a digital structured questionnaire was sent out to innovators to establish individual knowledge and experience with medical device innovation and regulation. Then, a single focus group discussion involving both medical device innovators and regulators to collect data about the current regulatory practices for medical devices in Uganda. Univariate and bivariate analysis was done for the quantitative data to summarize results in graphs and tables. Qualitative data was analyzed using thematic analysis. Ethical review and approval were obtained from the Makerere University School of Biomedical Sciences, Research and Ethics Committee, and the Uganda National Council for Science and Technology.
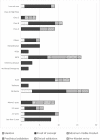
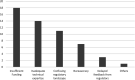
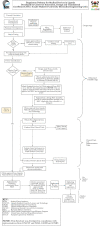
Results: A total of 47 innovators responded to the questionnaire. 14 respondents were excluded since they were not medical device innovators. Majority (76%) of individuals had been innovators for more than a year, held a bachelor's degree with a background in Engineering and applied sciences, and worked in an academic research institute. 22 of the 33 medical device innovators had stopped working on their innovations and had stalled at the proof-of-concept stage. Insufficient funding, inadequate technical expertise and confusing regulatory landscape were major challenges to innovation. The two themes that emerged from the discussion were "developing standards for medical devices regulation" and "implementation of regulations in practical processes". Legal limitations, lengthy processes, and low demand were identified as challenges to developing medical device regulations.
Conclusions: Efforts have been taken by government to create a pathway for medical device innovations to be translated to the market. More work needs to be done to coordinate efforts among stakeholders to build effective medical device regulations in Uganda.
Keywords: clinical evaluation; medical device standards; medical devices; medical devices regulations; medical innovation; regulatory pathway.
© 2023 Mpaata, Matovu, Takuwa, Kiwanuka, Lewis, Norrie, Ononge, Tuck, Wolters, Desmulliez and Ssekitoleko.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Experiences of medical device innovators as they navigate the regulatory system in Uganda.Front Med Technol. 2023 Apr 27;5:1162174. doi: 10.3389/fmedt.2023.1162174. eCollection 2023. Front Med Technol. 2023. PMID: 37181098 Free PMC article.
-
Translating medical device innovations to market - a Ugandan perspective.BMC Res Notes. 2023 Oct 9;16(1):262. doi: 10.1186/s13104-023-06541-6. BMC Res Notes. 2023. PMID: 37814313 Free PMC article.
-
Qualitative Study.2022 Sep 18. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2022 Sep 18. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 29262162 Free Books & Documents.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
The Challenges and Opportunities in Pediatric Medical Device Innovation: Monitoring Devices.Ann Thorac Surg. 2024 Dec 21:S0003-4975(24)01105-6. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2024.11.034. Online ahead of print. Ann Thorac Surg. 2024. PMID: 39716532 Review.
Cited by
-
Experiences of medical device innovators as they navigate the regulatory system in Uganda.Front Med Technol. 2023 Apr 27;5:1162174. doi: 10.3389/fmedt.2023.1162174. eCollection 2023. Front Med Technol. 2023. PMID: 37181098 Free PMC article.
-
A compound analysis of medical device clinical trials registered in Africa on clinicaltrials.gov.Trials. 2024 Oct 4;25(1):658. doi: 10.1186/s13063-024-08427-9. Trials. 2024. PMID: 39367383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Translating medical device innovations to market - a Ugandan perspective.BMC Res Notes. 2023 Oct 9;16(1):262. doi: 10.1186/s13104-023-06541-6. BMC Res Notes. 2023. PMID: 37814313 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lissel A, Ottenberg F, Bracio B, Ravizza A, de Maria C, Ahluwalia A, et al. Status and solutions to medical device regulations for improving the healthcare landscape in Africa. In: Conference proceedings: annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society conference. (2016). p. 4329–32. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Medical device technical series: development of medical device policies. In: K Lashley, editor. Geneva: World Health Organization; (2011). 45 p. [cited 2022 Aug 10]. Available at: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241501637.
-
- Janarthanan S, Kamaraj R. Medical device regulation in U.S. Res J Pharm Technol. (2020) 13(9):4453–6. 10.5958/0974-360X.2020.00786.6 - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources