Factors Related to Resuscitation Success and Prognosis of Cardiopulmonary Arrest Cases
- PMID: 36756484
- PMCID: PMC9886048
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-24382
Factors Related to Resuscitation Success and Prognosis of Cardiopulmonary Arrest Cases
Abstract
Background: In cases where return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) is provided in the Emergency Department (ED) after cardiopulmonary arrest (CA), it is important to investigate the parameters affecting ROSC rates, to determine the factors affecting the survival status and prognosis in the short and medium term, and to determine to what extent these factors affect the prognosis.
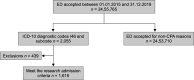
Materials and methods: This is a cross-sectional study that retrospectively investigates the factors affecting the success of resuscitation over a 5-year period in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) cases.
Results: We determined that ROSC was achieved in 26.1% of 1616 adult cardiopulmonary arrest cases, 14.8% survived the first 24 hours, and 3.8% were discharged from the hospital.
Conclusion: We determined that ROSC decreased by 21% with a 1-mg increase in the amount of adrenaline used, by 98% with a 1 mmol/L increase in HCO3 (std) value, by 27% with a 1 mmol/L increase in BE (B) value, and by 15% with a 1 mmol/L increase in lactate value. In terms of short-term survival, we found that a 1 mmol/L increase in lactate value reduced the probability of survival by 12%, and a 1 mEq/L increase in K value decreased the probability by 29%. With regard to the probability of survival in the medium term, we determined that the growth in age by 1 year decreased the probability by 4%, and the increase in K value by 1 mEq/L decreased the probability by 35%.
How to cite this article: Tekin FC, Köylü R, Köylü O, Kunt M. Factors Related to Resuscitation Success and Prognosis of Cardiopulmonary Arrest Cases. Indian J Crit Care Med 2023;27(1):26-31.
Keywords: Cardiopulmonary arrest; Clinical outcomes; Prognosis; Resuscitation.
Copyright © 2023; The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: None
Figures
References
-
- Hall JE, Guyton AC. Textbook of Medical Physiology. 11th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders; 2006.
-
- Güler K, Çalangu S. Acil Dahiliye. 7.baskı. İstanbul: Nobel TıpKitabevi; 2009.
-
- Tanrıöver MD. Kardiyak Arrest Öncesinde Kötülesen Hastayi Tanimak: Öngörü Kriterlerive Risk Factörleri/Recognizing the deteriorating patient prior to cardiac arrest: Predictive criteria and risk factors. J Crit Intens Care. 2011;2(1)
-
- Karataş M, Selçuk EB. Kardiyopulmoner resüsitasyonuntarihçesi. Kafkas Tıp Bilimleri Dergisi. 2012;(2):84–87.
-
- Tintinalli J, Stapczynski JS, Ma OJ, Cline D, Cydulka R, Meckler G. Tintinalli's Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Study Guide. 7th ed., New York: McGraw-Hill Medical; 2012.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials