Therapeutic properties and pharmacological activities of asiaticoside and madecassoside: A review
- PMID: 36756687
- PMCID: PMC9983323
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.17635
Therapeutic properties and pharmacological activities of asiaticoside and madecassoside: A review
Abstract
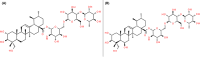
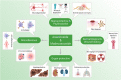
Centella asiatica is an ethnomedicinal herbaceous species that grows abundantly in tropical and sub-tropical regions of China, India, South-Eastern Asia and Africa. It is a popular nutraceutical that is employed in various forms of clinical and cosmetic treatments. C. asiatica extracts are reported widely in Ayurvedic and Chinese traditional medicine to boost memory, prevent cognitive deficits and improve brain functions. The major bioactive constituents of C. asiatica are the pentacyclic triterpenoid glycosides, asiaticoside and madecassoside, and their corresponding aglycones, asiatic acid and madecassic acid. Asiaticoside and madecassoside have been identified as the marker compounds of C. asiatica in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia and these triterpene compounds offer a wide range of pharmacological properties, including neuroprotective, cardioprotective, hepatoprotective, wound healing, anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, anti-allergic, anti-depressant, anxiolytic, antifibrotic, antibacterial, anti-arthritic, anti-tumour and immunomodulatory activities. Asiaticoside and madecassoside are also used extensively in treating skin abnormalities, burn injuries, ischaemia, ulcers, asthma, lupus, psoriasis and scleroderma. Besides medicinal applications, these phytocompounds are considered cosmetically beneficial for their role in anti-ageing, skin hydration, collagen synthesis, UV protection and curing scars. Existing reports and experimental studies on these compounds between 2005 and 2022 have been selectively reviewed in this article to provide a comprehensive overview of the numerous therapeutic advantages of asiaticoside and madecassoside and their potential roles in the medical future.
Keywords: Centella asiatica; asiaticoside; cardioprotective; madecassoside; neuroprotective; skin.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- James J, Dubery I. Identification and quantification of triterpenoid Centelloids in Centella asiatica (L.) urban by densitometric TLC. J Planar Chromat. 2011;24:82‐87. doi:10.1556/JPC.24.2011.1.16 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources