Established and Emerging Cancer Therapies and Cardiovascular System: Focus on Hypertension-Mechanisms and Mitigation
- PMID: 36756872
- PMCID: PMC10023512
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.122.17947
Established and Emerging Cancer Therapies and Cardiovascular System: Focus on Hypertension-Mechanisms and Mitigation
Abstract
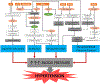
Cardiovascular disease and cancer are 2 of the leading causes of death worldwide. Although improvements in outcomes have been noted for both disease entities, the success of cancer therapies has come at the cost of at times very impactful adverse events such as cardiovascular events. Hypertension has been noted as both, a side effect as well as a risk factor for the cardiotoxicity of cancer therapies. Some of these dynamics are in keeping with the role of hypertension as a cardiovascular risk factor not only for heart failure, but also for the development of coronary and cerebrovascular disease, and kidney disease and its association with a higher morbidity and mortality overall. Other aspects such as the molecular mechanisms underlying the amplification of acute and long-term cardiotoxicity risk of anthracyclines and increase in blood pressure with various cancer therapeutics remain to be elucidated. In this review, we cover the latest clinical data regarding the risk of hypertension across a spectrum of novel anticancer therapies as well as the underlying known or postulated pathophysiological mechanisms. Furthermore, we review the acute and long-term implications for the amplification of the development of cardiotoxicity with drugs not commonly associated with hypertension such as anthracyclines. An outline of management strategies, including pharmacological and lifestyle interventions as well as models of care aimed to facilitate early detection and more timely management of hypertension in patients with cancer and survivors concludes this review, which overall aims to improve both cardiovascular and cancer-specific outcomes.
Keywords: blood pressure; cardiovascular diseases; epidemiology; hypertension; neoplasms; risk factor; treatment.
Figures


References
-
- Roth GA, Abate D, Abate KH, Abay SM, Abbafati C, Abbasi N, Abbastabar H, Abd-Allah L, Abdela J, Abdelalim A, et al. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1736–1788. doi: Doi 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32203-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lancellotti P, Nguyen Trung M-L, Oury C, Moonen M. Cancer and cardiovascular mortality risk: is the die cast? European Heart Journal. 2021;42:110–112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

