A pilot sentinel surveillance system to monitor treatment and treatment outcomes of chronic hepatitis B and C infections in clinical centres in three European countries, 2019
- PMID: 36757314
- PMCID: PMC9912376
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2023.28.6.2200184
A pilot sentinel surveillance system to monitor treatment and treatment outcomes of chronic hepatitis B and C infections in clinical centres in three European countries, 2019
Abstract
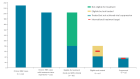
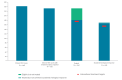
BackgroundThe World Health Organization European Action Plan 2020 targets for the elimination of viral hepatitis are that > 75% of eligible individuals with chronic hepatitis B (HBV) or hepatitis C (HCV) are treated, of whom > 90% achieve viral suppression.AimTo report the results from a pilot sentinel surveillance to monitor chronic HBV and HCV treatment uptake and outcomes in 2019.MethodsWe undertook retrospective enhanced data collection on patients with a confirmed chronic HBV or HCV infection presenting at one of seven clinics in three countries (Croatia, Romania and Spain) for the first time between 1 January 2019 and 30 June 2019. Clinical records were reviewed from date of first attendance to 31 December 2019 and data on sociodemographics, clinical history, laboratory results, treatment and treatment outcomes were collected. Treatment eligibility, uptake and case outcome were assessed.ResultsOf 229 individuals with chronic HBV infection, treatment status was reported for 203 (89%). Of the 80 individuals reported as eligible for treatment, 51% (41/80) were treated of whom 89% (33/37) had achieved viral suppression. Of 240 individuals with chronic HCV infection, treatment status was reported for 231 (96%). Of 231 eligible individuals, 77% (179/231) were treated, the majority of whom had received direct acting antivirals (99%, 174/176) and had achieved sustained virological response (98%, 165/169).ConclusionTreatment targets for global elimination were missed for HBV but not for HCV. A wider European implementation of sentinel surveillance with a representative sample of sites could help monitor progress towards achieving hepatitis control targets.
Keywords: hepatitis B; hepatitis C; surveillance; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Maria Buti: advisor and speaker for Gilead Sciences and Abbvie.
All other authors: no conflict of interest declared.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global progress report on HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections, 2021. Accountability for the global health sector strategies 2016-2021: actions for impact. Geneva: WHO; 2021. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240027077
-
- Hofstraat SHI, Falla AM, Duffell EF, Hahné SJM, Amato-Gauci AJ, Veldhuijzen IK, et al. Current prevalence of chronic hepatitis B and C virus infection in the general population, blood donors and pregnant women in the EU/EEA: a systematic review. Epidemiol Infect. 2017;145(14):2873-85. 10.1017/S0950268817001947 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
