Changes in Retinal Sensitivity Associated With Cotoretigene Toliparvovec in X-Linked Retinitis Pigmentosa With RPGR Gene Variations
- PMID: 36757689
- PMCID: PMC9912164
- DOI: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2022.6254
Changes in Retinal Sensitivity Associated With Cotoretigene Toliparvovec in X-Linked Retinitis Pigmentosa With RPGR Gene Variations
Erratum in
-
Error in Spelling of Nonauthor Collaborator Name.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2023 Mar 1;141(3):293. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2023.0716. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 36928997 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Importance: X-linked retinitis pigmentosa (XLRP) is a severe cause of early-onset RP in male individuals, characterized by degeneration of photoreceptors, an extinguished electroretinogram, and vision loss.
Objective: To assess the duration of improvements in retinal sensitivity associated with a single, subretinal injection of cotoretigene toliparvovec (BIIB112/AAV8-RPGR) gene therapy after vitrectomy surgery in the dosed eye over 12 months in part 1 of the Clinical Trial of Retinal Gene Therapy for X-linked Retinitis Pigmentosa Using BIIB112 (XIRIUS) study, compared with untreated fellow eyes and eyes from the untreated subgroup from the Natural History of the Progression of X-Linked Retinitis Pigmentosa (XOLARIS) study.
Design, setting, and participants: This was a post hoc analysis of the XIRIUS and XOLARIS studies. Part 1 of the XIRIUS study was a phase 1, dose-escalation study of 18 male participants 18 years or older enrolled between March 8, 2017, and October 16, 2018, with genetically confirmed RPGR-variant XLRP with active disease and best-corrected visual acuity better than or equal to light perception (cohort 1), 34 to 73 letters (20/40 to 20/200 Snellen equivalent; cohorts 2-3), or greater than or equal to 34 letters (better than or equal to 20/200 Snellen equivalent; cohorts 4-6). Participants from the noninterventional, multicenter, global, prospective XOLARIS clinical study who met the inclusion and exclusion criteria of part 1 of XIRIUS were included as a comparator group (n = 103). Safety assessments included all XIRIUS participants; post hoc associations of retinal sensitivity assessments in XIRIUS only included the 12 participants receiving the 4 highest doses of cotoretigene toliparvovec. Data were analyzed on June 30, 2021.
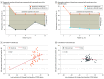
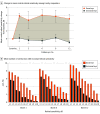
Main outcomes and measures: Incidence of dose-limiting toxicities (DLTs), treatment-emergent adverse events, changes from baseline in retinal sensitivity (as assessed by macular integrity assessment microperimetry), retinal sensitivity response (achievement of ≥7-dB improvement from baseline at ≥5 of 16 central loci), and low-luminance visual acuity were assessed over 24 months.
Results: A total of 18 participants (mean [SD] age, 31.9 [9.4] years; male, 100%) were enrolled and completed the XIRIUS study. A subgroup of 103 participants (mean [SD] age, 30.8 [11.4] years; male, 100%) from the XOLARIS study was included. Administration of the 4 highest doses of cotoretigene toliparvovec (n = 12) among the 18 XIRIUS participants was associated with early improvements in retinal sensitivity. One of 103 untreated participants (1%) in the XOLARIS subgroup achieved improved retinal sensitivity at month 12. No DLTs were noted at any dose, and serious adverse events of reduced visual acuity (n = 2) and noninfective retinitis (n = 1) occurred.
Conclusions and relevance: Results suggest that early and sustained improvements in retinal sensitivity and low-luminance visual acuity in some participants through 12 months support consideration of additional clinical trials.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: XIRIUS: NCT03116113; XOLARIS: NCT04926129.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Comment in
-
Perspectives on Evolving Gene Therapy for X-Linked Retinitis Pigmentosa.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2023 Mar 1;141(3):283-284. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2022.6436. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 36757711 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

