EMT-activated secretory and endocytic vesicular trafficking programs underlie a vulnerability to PI4K2A antagonism in lung cancer
- PMID: 36757799
- PMCID: PMC10065074
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI165863
EMT-activated secretory and endocytic vesicular trafficking programs underlie a vulnerability to PI4K2A antagonism in lung cancer
Abstract
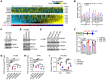
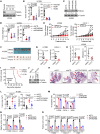
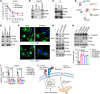
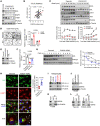
Hypersecretory malignant cells underlie therapeutic resistance, metastasis, and poor clinical outcomes. However, the molecular basis for malignant hypersecretion remains obscure. Here, we showed that epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) initiates exocytic and endocytic vesicular trafficking programs in lung cancer. The EMT-activating transcription factor zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 1 (ZEB1) executed a PI4KIIIβ-to-PI4KIIα (PI4K2A) dependency switch that drove PI4P synthesis in the Golgi and endosomes. EMT enhanced the vulnerability of lung cancer cells to PI4K2A small-molecule antagonists. PI4K2A formed a MYOIIA-containing protein complex that facilitated secretory vesicle biogenesis in the Golgi, thereby establishing a hypersecretory state involving osteopontin (SPP1) and other prometastatic ligands. In the endosomal compartment, PI4K2A accelerated recycling of SPP1 receptors to complete an SPP1-dependent autocrine loop and interacted with HSP90 to prevent lysosomal degradation of AXL receptor tyrosine kinase, a driver of cell migration. These results show that EMT coordinates exocytic and endocytic vesicular trafficking to establish a therapeutically actionable hypersecretory state that drives lung cancer progression.
Keywords: Cancer gene therapy; Cell Biology; Lung cancer; Oncogenes; Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Comment in
-
PI4K2A: a novel potential therapeutic target for lung cancer.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024 Jan 31;13(1):199-204. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-23-734. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38404996 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

