TFIID dependency of steady-state mRNA transcription altered epigenetically by simultaneous functional loss of Taf1 and Spt3 is Hsp104-dependent
- PMID: 36757926
- PMCID: PMC9910645
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281233
TFIID dependency of steady-state mRNA transcription altered epigenetically by simultaneous functional loss of Taf1 and Spt3 is Hsp104-dependent
Abstract
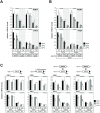
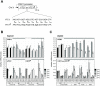
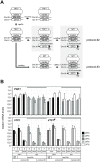
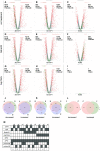
In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, class II gene promoters have been divided into two subclasses, TFIID- and SAGA-dominated promoters or TFIID-dependent and coactivator-redundant promoters, depending on the experimental methods used to measure mRNA levels. A prior study demonstrated that Spt3, a TBP-delivering subunit of SAGA, functionally regulates the PGK1 promoter via two mechanisms: by stimulating TATA box-dependent transcriptional activity and conferring Taf1/TFIID independence. However, only the former could be restored by plasmid-borne SPT3. In the present study, we sought to determine why ectopically expressed SPT3 is unable to restore Taf1/TFIID independence to the PGK1 promoter, identifying that this function was dependent on the construction protocol for the SPT3 taf1 strain. Specifically, simultaneous functional loss of Spt3 and Taf1 during strain construction was a prerequisite to render the PGK1 promoter Taf1/TFIID-dependent in this strain. Intriguingly, genetic approaches revealed that an as-yet unidentified trans-acting factor reprogrammed the transcriptional mode of the PGK1 promoter from the Taf1/TFIID-independent state to the Taf1/TFIID-dependent state. This factor was generated in the haploid SPT3 taf1 strain in an Hsp104-dependent manner and inherited meiotically in a non-Mendelian fashion. Furthermore, RNA-seq analyses demonstrated that this factor likely affects the transcription mode of not only the PGK1 promoter, but also of many other class II gene promoters. Collectively, these findings suggest that a prion or biomolecular condensate is generated in a Hsp104-dependent manner upon simultaneous functional loss of TFIID and SAGA, and could alter the roles of these transcription complexes on a wide variety of class II gene promoters without altering their primary sequences. Therefore, these findings could provide the first evidence that TFIID dependence of class II gene transcription can be altered epigenetically, at least in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Copyright: © 2023 Iwami et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The function of Spt3, a subunit of the SAGA complex, in PGK1 transcription is restored only partially when reintroduced by plasmid into taf1 spt3 double mutant yeast strains.Genes Genet Syst. 2020 Aug 27;95(3):151-163. doi: 10.1266/ggs.20-00004. Epub 2020 Jul 4. Genes Genet Syst. 2020. PMID: 32624556
-
SAGA subunits Spt3 and Spt8 act directly and non-redundantly with TFIID in TBP recruitment in the Gcn4 transcriptome.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jul 8;53(13):gkaf598. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf598. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40637224 Free PMC article.
-
SAGA mediates transcription from the TATA-like element independently of Taf1p/TFIID but dependent on core promoter structures in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.PLoS One. 2017 Nov 27;12(11):e0188435. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188435. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29176831 Free PMC article.
-
Architecture of the multi-functional SAGA complex and the molecular mechanism of holding TBP.FEBS J. 2021 May;288(10):3135-3147. doi: 10.1111/febs.15563. Epub 2020 Sep 29. FEBS J. 2021. PMID: 32946670 Review.
-
SAGA and TFIID: Friends of TBP drifting apart.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2021 Feb;1864(2):194604. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2020.194604. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2021. PMID: 32673655 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

