Alkyne Derivatives of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors Including Nirmatrelvir Inhibit by Reacting Covalently with the Nucleophilic Cysteine
- PMID: 36757959
- PMCID: PMC9924091
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01627
Alkyne Derivatives of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease Inhibitors Including Nirmatrelvir Inhibit by Reacting Covalently with the Nucleophilic Cysteine
Abstract
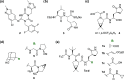
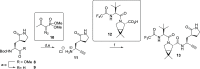
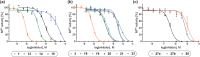
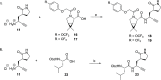
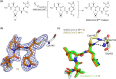
Nirmatrelvir (PF-07321332) is a nitrile-bearing small-molecule inhibitor that, in combination with ritonavir, is used to treat infections by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2). Nirmatrelvir interrupts the viral life cycle by inhibiting the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro), which is essential for processing viral polyproteins into functional nonstructural proteins. We report studies which reveal that derivatives of nirmatrelvir and other Mpro inhibitors with a nonactivated terminal alkyne group positioned similarly to the electrophilic nitrile of nirmatrelvir can efficiently inhibit isolated Mpro and SARS-CoV-2 replication in cells. Mass spectrometric and crystallographic evidence shows that the alkyne derivatives inhibit Mpro by apparent irreversible covalent reactions with the active site cysteine (Cys145), while the analogous nitriles react reversibly. The results highlight the potential for irreversible covalent inhibition of Mpro and other nucleophilic cysteine proteases by alkynes, which, in contrast to nitriles, can be functionalized at their terminal position to optimize inhibition and selectivity, as well as pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Owen D. R.; Allerton C. M. N.; Anderson A. S.; Aschenbrenner L.; Avery M.; Berritt S.; Boras B.; Cardin R. D.; Carlo A.; Coffman K. J.; Dantonio A.; Di L.; Eng H.; Ferre R.; Gajiwala K. S.; Gibson S. A.; Greasley S. E.; Hurst B. L.; Kadar E. P.; Kalgutkar A. S.; Lee J. C.; Lee J.; Liu W.; Mason S. W.; Noell S.; Novak J. J.; Obach R. S.; Ogilvie K.; Patel N. C.; Pettersson M.; Rai D. K.; Reese M. R.; Sammons M. F.; Sathish J. G.; Singh R. S. P.; Steppan C. M.; Stewart A. E.; Tuttle J. B.; Updyke L.; Verhoest P. R.; Wei L.; Yang Q.; Zhu Y. An oral SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19. Science 2021, 374, 1586–1593. 10.1126/science.abl4784. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gorbalenya A. E.; Baker S. C.; Baric R. S.; de Groot R. J.; Drosten C.; Gulyaeva A. A.; Haagmans B. L.; Lauber C.; Leontovich A. M.; Neuman B. W.; Penzar D.; Perlman S.; Poon L. L. M.; Samborskiy D. V.; Sidorov I. A.; Sola I.; Ziebuhr J. The species severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 536–544. 10.1038/s41564-020-0695-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- C8717/A18245/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- BB/M011224/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- 106244/Z/14/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- BB/J003018/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Medical
Miscellaneous

