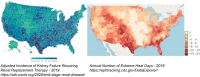
Extreme Heat Can Exacerbate Disproportionate Burden of Severe Kidney Disease in Historically Marginalized Communities: Call to Action
- PMID: 36758149
- PMCID: PMC10564337
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.0000000000000113
Extreme Heat Can Exacerbate Disproportionate Burden of Severe Kidney Disease in Historically Marginalized Communities: Call to Action
Figures
References
-
- American Society of Nephrology. Statement on Climate Change. 2022. https://www.asn-online.org/about/press/releases/ASN_PR_20220525_Climatec.... Accessed January 13, 2023.
-
- Hoffman JS, Shandas V, Pendleton N. The effects of historical housing policies on resident exposure to intra-urban heat: a study of 108 US urban areas. Climate. 2020;8(1):12. doi:10.3390/cli8010012 - DOI
-
- Moghani Lankarani M, Assari S. Diabetes, hypertension, obesity, and long-term risk of renal disease mortality: racial and socioeconomic differences. J Diabetes Investig. 2017;8(4):590–599. doi:10.1111/jdi.12618 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sorensen C, Garcia-Trabanino R. A new era of climate medicine—addressing heat-triggered renal disease. New Engl J Med. 2019;381(8):693–696. doi:10.1056/nejmp1907859 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shandas V, Voelkel J, Williams J, Hoffman J. Integrating satellite and ground measurements for predicting locations of extreme urban heat. Climate. 2019;7(1):5. doi:10.3390/cli7010005 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous