Longitudinal comparison of the developing gut virome in infants and their mothers
- PMID: 36758519
- PMCID: PMC9950819
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2023.01.003
Longitudinal comparison of the developing gut virome in infants and their mothers
Abstract
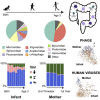
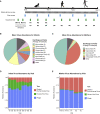
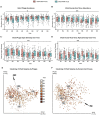
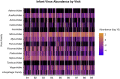
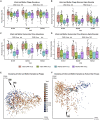
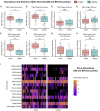
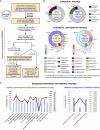
The human gut virome and its early life development are poorly understood. Prior studies have captured single-point assessments with the evolution of the infant virome remaining largely unexplored. We performed viral metagenomic sequencing on stool samples collected longitudinally from a cohort of 53 infants from age 2 weeks to 3 years (80.7 billion reads), and from their mothers (9.8 billion reads) to examine and compare viromes. The asymptomatic infant virome consisted of bacteriophages, nonhuman dietary/environmental viruses, and human-host viruses, predominantly picornaviruses. In contrast, human-host viruses were largely absent from the maternal virome. Previously undescribed, sequence-divergent vertebrate viruses were detected in the maternal but not infant virome. As infants aged, the phage component evolved to resemble the maternal virome, but by age 3, the human-host component remained dissimilar from the maternal virome. Thus, early life virome development is determined predominantly by dietary, infectious, and environmental factors rather than direct maternal acquisition.
Keywords: SURPI; alpha diversity; bacteriophages; beta diversity; infant gut virome; maternal virome; metagenomic sequencing; microbiome; microviruses; parechovirus; picornaviruses; principal component analysis.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests S.F., D.S., and C.Y.C. are co-inventors on US patent 11,380,421, “Pathogen Detection using Next Generation Sequencing,” under which algorithms for taxonomic classification, filtering, and pathogen detection are used by SURPI+ software for virus identification from metagenomic data.
Figures
References
-
- Milani C., Duranti S., Bottacini F., Casey E., Turroni F., Mahony J., Belzer C., Delgado Palacio S., Arboleya Montes S., Mancabelli L., et al. The first microbial colonizers of the human gut: composition, activities, and health implications of the infant gut microbiota. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017;81 doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00036-17. e00036-17. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

