Clinical Outcomes of Intrascleral Fixation of Intraocular Lens Compared to Ciliary Sulcus Implantation and Transscleral Fixation
- PMID: 36758538
- PMCID: PMC10151168
- DOI: 10.3341/kjo.2022.0093
Clinical Outcomes of Intrascleral Fixation of Intraocular Lens Compared to Ciliary Sulcus Implantation and Transscleral Fixation
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the clinical outcomes of intrascleral fixation of the three-piece intraocular lenses (IOLs) 2.5 mm posterior to the limbus with ciliary sulcus implantation and transscleral fixation 2.5 mm posterior to the limbus.
Methods: Sixty-five eyes of 65 patients who underwent ciliary sulcus implantation or transscleral or intrascleral fixation of the AMO Sensar AR40e IOL were retrospectively reviewed. The postoperative refractive prediction error, back-calculated effective lens position (ELP), corrected distance visual acuity (CDVA), and postoperative residual cylinder were compared.
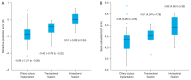
Results: There were significant differences in the median (interquartile range) postoperative refractive prediction error (diopters [D]) among the three groups (p < 0.001): for ciliary sulcus implantation (33 eyes), -0.89 D (-1.21 to -0.56 D); for transscleral fixation (10 eyes), -0.40 D (-0.78 to -0.22 D); and for intrascleral fixation (22 eyes), 0.01 D (-0.28 to 0.34 D). Significant differences (p < 0.001) were observed in the median back-calculated ELP: for ciliary sulcus implantation, 4.35 mm (3.95 to 4.55 mm); for transscleral fixation, 4.51 mm (4.34 to 4.76 mm); and for intrascleral fixation, 4.90 mm (4.56 to 5.35 mm). There were no differences in the median postoperative CDVA (0, 0.10, and 0 logarithm of the minimum angle of resolution, respectively; p = 0.083) and the residual cylinder (-0.75, -1.50, and -0.63 D, respectively; p = 0.074) among three groups.
Conclusions: Intrascleral fixation showed no myopic shift and the most posterior lens position, while ciliary sulcus implantation induced the greatest myopic shift and the most anterior lens position. However, there was no significant difference in the postoperative CDVA or astigmatism among the eyes with different IOL insertion methods, demonstrating good IOL stability and vision outcomes.
Keywords: Fixation; Intraocular lens; Intrascleral; Sulcus; Transscleral.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Por YM, Lavin MJ. Techniques of intraocular lens suspension in the absence of capsular/zonular support. Surv Ophthalmol. 2005;50:429–62. - PubMed
-
- Park SY, Eom Y, Lee YJ, et al. Scleral fixation of subluxated or dislocated multifocal and multifocal toric intraocular lenses. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2022;260:1195–203. - PubMed
-
- Smiddy WE, Sawusch MR, O’Brien TP, et al. Implantation of scleral-fixated posterior chamber intraocular lenses. J Cataract Refract Surg. 1990;16:691–6. - PubMed
-
- Gabor SG, Pavlidis MM. Sutureless intrascleral posterior chamber intraocular lens fixation. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2007;33:1851–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 13-2020-007/Seoul National University Bundang Hospital
- K2107901/College of Medicine, Korea University
- Korea Institute of Science and Technology
- K1625491/Korea University
- K1722121/Korea University
- K1811051/Korea University
- K1913161/Korea University
- K2010921/Korea University
- Ministry of Science and ICT
- Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy
- 1711174253/Ministry of Health and Welfare
- RS2020-KD000296/Ministry of Health and Welfare
- Ministry of Food and Drug Safety
- 2020002960007/Korea Environmental Industry and Technology Insitute
- NTIS-1485018521/Korea Environmental Industry and Technology Insitute
- Ministry of Environment
- 2021R1F1A1062017/National Research Foundation of Korea
- S3127902/Ministry of SMEs and Startups
- S3305836/Ministry of SMEs and Startups
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical