Severe allergic dysregulation due to a gain of function mutation in the transcription factor STAT6
- PMID: 36758835
- PMCID: PMC10330134
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2023.01.023
Severe allergic dysregulation due to a gain of function mutation in the transcription factor STAT6
Abstract
Background: Inborn errors of immunity have been implicated in causing immune dysregulation, including allergic diseases. STAT6 is a key regulator of allergic responses.
Objectives: This study sought to characterize a novel gain-of-function STAT6 mutation identified in a child with severe allergic manifestations.
Methods: Whole-exome and targeted gene sequencing, lymphocyte characterization, and molecular and functional analyses of mutated STAT6 were performed.
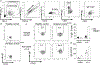
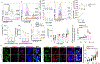
Results: This study reports a child with a missense mutation in the DNA binding domain of STAT6 (c.1114G>A, p.E372K) who presented with severe atopic dermatitis, eosinophilia, and elevated IgE. Naive lymphocytes from the affected patient displayed increased TH2- and suppressed TH1- and TH17-cell responses. The mutation augmented both basal and cytokine-induced STAT6 phosphorylation without affecting dephosphorylation kinetics. Treatment with the Janus kinase 1/2 inhibitor ruxolitinib reversed STAT6 hyperresponsiveness to IL-4, normalized TH1 and TH17 cells, suppressed the eosinophilia, and improved the patient's atopic dermatitis.
Conclusions: This study identified a novel inborn error of immunity due to a STAT6 gain-of-function mutation that gave rise to severe allergic dysregulation. Janus kinase inhibitor therapy could represent an effective targeted treatment for this disorder.
Keywords: Inborn errors of immunity; Jakinibs; Janus kinase inhibitors; STAT6; gain-of-function mutation; primary atopic disorders.
Copyright © 2023 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

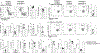
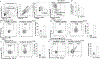

Comment in
-
STAT6 joins the gain-of-function club.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023 Jul;152(1):53-55. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2023.05.003. Epub 2023 May 14. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37192684 No abstract available.
References
-
- Vaseghi-Shanjani M, Snow AL, Margolis DJ, Latrous M, Milner JD, Turvey SE, et al. Atopy as Immune Dysregulation: Offender Genes and Targets. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 2022; 10:1737–56. - PubMed
-
- Holland SM, DeLeo FR, Elloumi HZ, Hsu AP, Uzel G, Brodsky N, et al. STAT3 mutations in the hyper-IgE syndrome. N Engl J Med 2007; 357:1608–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

