Identification of a virulent phage infecting species of Nitrosomonas
- PMID: 36759553
- PMCID: PMC10119301
- DOI: 10.1038/s41396-023-01380-6
Identification of a virulent phage infecting species of Nitrosomonas
Abstract
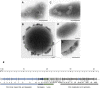
In the first and limiting step of nitrification, ammonia (NH3) is oxidised to nitrite (NO2-) by the action of some prokaryotes, including bacteria of the Nitrosomonas genus. A potential approach to nitrification inhibition would be through the application of phages, but until now this method has been unexplored and no virulent phages that infect nitrifying bacteria have been described. In this study, we report the isolation of the first phage infecting some Nitrosomonas species. This polyvalent virulent phage (named ΦNF-1) infected Nitrosomonas europaea, Nitrosomonas communis, and Nitrosomonas nitrosa. Phage ΦNF-1 has the morphology of the Podoviridae family, a dsDNA genome of 41,596 bp and a 45.1 % GC content, with 50 predicted open reading frames. Phage ΦNF-1 was found to inhibit bacterial growth and reduce NH4+ consumption in the phage-treated cultures. The application of phages as biocontrol agents could be a useful strategy for nitrification inhibition without the restrictions associated with chemical inhibitors.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to International Society for Microbial Ecology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Rowan AK, Snape JR, Fearnside D, Barer MR, Curtis TP, Head IM. Composition and diversity of ammonia-oxidising bacterial communities in wastewater treatment reactors of different design treating identical wastewater. FEMS Microbiol Ecol. 2003;43:195–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2003.tb01059.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- de Boer W, Kowalchuk GA. Nitrification in acid soils: microorganisms and mechanisms. Soil Biol Biochem. 2001;33:853–66. doi: 10.1016/S0038-0717(00)00247-9. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

