Association of chorioretinal thickness with chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 36759800
- PMCID: PMC9909840
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-023-02802-x
Association of chorioretinal thickness with chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Objective: To assess retinal and choroidal thickness changes in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients using spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT).
Background: CKD is a devastating health trouble. The eye and the kidney share similar structural and genetic pathways, so that kidney disease and ocular disease may be closely linked. OCT is a precise, fast method for high-definition scanning of the retina and choroid.
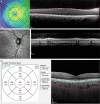
Patients and methods: A cross sectional study was conducted at Menoufia University Hospital ophthalmology department on 144 eyes of 72 CKD patients divided into 3 groups according to the stage of CKD as follows: group 1: CKD stage 1-2, with Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) > 60 ml/min/1.73m2 group 2: CKD stage 3, GFR 30-59 ml/min/1.73m2 and group 3: CKD stage 4-5, eGFR < 29 ml/min/1.73m2. All patients underwent full ophthalmologic examination followed by OCT assessment of retinal, retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) and choroidal thickness.
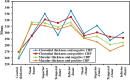
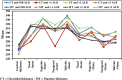
Results: Retinal and choroidal thickness were reduced in group 2 (CKD stage 3) and group 3 (CKD stage 4-5) compared with group 1 (CKD stage 1-2). The reduction was more severe in group 3 than group 2. RNFL thickness did not differ between groups. A thinner retina and choroid were associated with an elevated serum C-reactive protein (CRP) concentration, and greater degrees of proteinuria.
Conclusion: Chorioretinal thinning in CKD is associated with a lower eGFR, a higher CRP, and greater proteinuria. Further studies, in a large scale of patients, are needed to detect whether these eye changes reflect the natural history of CKD.
Keywords: Choroid; Chronic kidney disease; Optical coherence tomography; Retina; Retinal nerve fiber layer.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- National kidney foundation K / DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002;39(Suppl 1):S1–266. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

