Interleukin 6 and interferon gamma haplotypes are related to cytokine serum levels in dogs in an endemic Leishmania infantum region
- PMID: 36759910
- PMCID: PMC9911338
- DOI: 10.1186/s40249-023-01058-3
Interleukin 6 and interferon gamma haplotypes are related to cytokine serum levels in dogs in an endemic Leishmania infantum region
Abstract
Background: The Ibizan Hound is a canine breed native to the Mediterranean region, where leishmaniasis is an endemic zoonosis. Several studies indicate a low prevalence of this disease in Ibizan Hound dogs, whereas other canine breeds present a high prevalence. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms still remain unknown. The aim of this work is to analyse the relationship between serum levels of cytokines and the genomic profiles in two canine breeds, Ibizan Hound (resistant canine breed model) and Boxer (susceptible canine breed model).
Methods: In this study, we analyse the haplotypes of genes encoding cytokines related to immune response of Leishmania infantum infection in twenty-four Boxers and twenty-eight Ibizan Hounds apparently healthy using CanineHD DNA Analysis BeadChip including 165,480 mapped positions. The haplo.glm extension of haplo.score was used to perform a General Linear Model (GLM) regression to estimate the magnitude of individual haplotype effects within each cytokine.
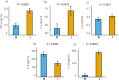
Results: Mean levels of interferon gamma (IFN-γ), interleukin 2 (IL-2) and IL-18 in Boxer dogs were 0.19 ± 0.05 ng/ml, 46.70 ± 4.54 ng/ml, and 36.37 ± 30.59 pg/ml, whereas Ibizan Hound dogs present 0.49 ± 0.05 ng/ml, 64.55 ± 4.54 ng/ml, and 492.10 ± 31.18 pg/ml, respectively. The GLM regression shows fifteen haplotypes with statistically significant effect on the cytokine serum levels (P < 0.05). The more relevant are IL6-CGAAG and IFNG-GCA haplotypes, which increase and decrease the IL-2, IL-8 and IFN-γ serum levels, respectively.
Conclusions: Haplotypes in the IFNG and IL6 genes have been correlated to serum levels of IFN-γ, IL-2 and IL-18, and a moderate effect has been found on IL8 haplotype correlated to IL-8 and IL-18 serum levels. The results indicate that the resistance to L. infantum infection could be a consequence of certain haplotypes with a high frequency in the Ibizan Hound dog breed, while susceptibility to the disease would be related to other specific haplotypes, with high frequency in Boxer. Future studies are needed to elucidate whether these differences and haplotypes are related to different phenotypes in immune response and expression gene regulation to L. infantum infections in dogs and their possible application in new treatments and vaccines.
Keywords: Cytokine; Dog; Haplotype; Immune response; Leishmania; Regulatory mechanism; Resistance; Susceptibility.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genetic haplotypes associated with immune response to Leishmania infantum infection in dogs.Vet Res Commun. 2023 Sep;47(3):1675-1685. doi: 10.1007/s11259-023-10123-z. Epub 2023 Apr 14. Vet Res Commun. 2023. PMID: 37059873
-
Serum levels and genetic variations of cytokines in two canine breeds (Ibizan hound and boxer) in the Mediterranean region, in terms of Leishmania infantum infection.Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2022 Nov-Dec;90-91:101908. doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2022.101908. Epub 2022 Nov 14. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 36410071
-
Immunological profile of two canine breeds in an endemic region of Leishmania infantum.Vet Parasitol Reg Stud Reports. 2023 May;40:100861. doi: 10.1016/j.vprsr.2023.100861. Epub 2023 Mar 28. Vet Parasitol Reg Stud Reports. 2023. PMID: 37068864
-
Canine susceptibility to visceral leishmaniasis: A systematic review upon genetic aspects, considering breed factors and immunological concepts.Infect Genet Evol. 2019 Oct;74:103293. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2017.10.005. Epub 2017 Oct 5. Infect Genet Evol. 2019. PMID: 28987807
-
Cutaneous immune mechanisms in canine leishmaniosis due to Leishmania infantum.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2015 Feb 15;163(3-4):94-102. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2014.11.011. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2015. PMID: 25555497 Review.
Cited by
-
An integrated analysis of the structural changes and gene expression of spleen in human visceral leishmaniasis with and without HIV coinfection.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 Jun 6;18(6):e0011877. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0011877. eCollection 2024 Jun. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 38843306 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Regulation of Immune Response in Dogs.Genes (Basel). 2025 Jun 29;16(7):764. doi: 10.3390/genes16070764. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40725420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Breed on Hematological and Biochemical Parameters of Apparently Healthy Dogs Infected with Zoonotic Pathogens Endemic to the Mediterranean Basin.Animals (Basel). 2024 May 21;14(11):1516. doi: 10.3390/ani14111516. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38891563 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maxfield L, Crane JS. Leishmaniasis. In: Maxfield L, editor. StatPearls. Treasure Island: StatPearls publishing; 2022.
-
- Burza S, Croft SL, Boelaert M. Leishmaniasis. Lancet. 2018;392:951–970. - PubMed
-
- https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/leishmaniasis. Accessed 07 Nov 2022.
-
- Mendoza-Roldan JA, Latrofa MS, Tarallo VD, Manoj RR, Bezerra-Santos MA, Annoscia G, et al. Leishmania spp. in Squamata reptiles from the Mediterranean basin. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2022;69:2856–2866. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

