Neuroprotective Efficacy of Europinidin in Streptozotocin-Induced Memory Impairment by Modulation of Oxidative Stress, Inflammatory Mediators, and Cholinesterase Activity in Rats
- PMID: 36760351
- PMCID: PMC9904885
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/5248127
Neuroprotective Efficacy of Europinidin in Streptozotocin-Induced Memory Impairment by Modulation of Oxidative Stress, Inflammatory Mediators, and Cholinesterase Activity in Rats
Abstract
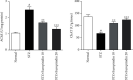
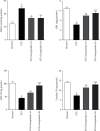
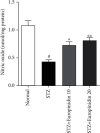
Materials and methods: Oral acute toxicity studies were performed to evaluate the toxicological effects of europinidin in animals. In this study, four different animal groups (n = 6) were used. Group I was the normal control, group II was the STZ-induced diabetes control, group III was STZ + europinidin-treated (10 mg/kg), and group IV was STZ + europinidin-treated (10 mg/kg). The efficacy of europinidin at a dose of 10 mg/kg and 20 mg/kg was studied with single-dose administration of streptozotocin, which experimentally induced memory impairments in Wistar male rats for 38 days. The mean body weight and blood glucose levels were recorded at the initial and end of the study. The two behavioural paradigms (Y-maze and Morris water maze) were performed to evaluate spatial and working memory in rats. The biochemical parameters such as acetylcholinesterase, choline acetyltransferase, superoxide dismutase, glutathione transferase, malonaldehyde, catalase, and nitric oxide level as hallmarks of oxidative stress were measured. Additionally, the proinflammatory parameters were also determined to evaluate the neuroinflammatory responses associated with streptozotocin such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin (IL-6), nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-ƙB), interleukin (IL-10), and nuclear factor-erythroid factor 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) in the perfused brain.
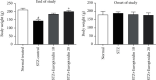
Results: The rats in the europinidin-treated group exhibited a significant restoration of body weight and blood glucose level as compared with the streptozotocin control group. Furthermore, europinidin significantly modulated the spatial and working memory in rats, when assessed through behavioural paradigms. Streptozotocin caused a significant alteration in biochemical, neuronal enzymatic, and neuroinflammatory parameters, which were significantly restored to normal levels by europinidin.
Conclusion: The present study attributed the neuroprotective efficacy of europinidin in experimental animal models by subsiding the several biomarkers of oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and neuronal enzymatic activities.
Copyright © 2023 Aftab Ahmad.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Rajesh V., Riju T., Venkatesh S., Babu G. Memory enhancing activity of Lawsonia inermis Linn. Leaves against scopolamine induced memory impairment in Swiss albino mice. Oriental Pharmacy and Experimental Medicine . 2017;17(2):127–142. doi: 10.1007/s13596-017-0268-8. - DOI
-
- Kidd P. M. Alzheimer’s disease, amnestic mild cognitive impairment, and age-associated memory impairment: current understanding and progress toward integrative prevention. Alternative Medicine Review . 2008;13 - PubMed
-
- Association Alzheimer. 2017 alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. . 2017;13(4):325–373. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2017.02.001. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

