UCHL1 regulated by Sp1 ameliorates cochlear hair cell senescence and oxidative damage
- PMID: 36761006
- PMCID: PMC9905655
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2023.11793
UCHL1 regulated by Sp1 ameliorates cochlear hair cell senescence and oxidative damage
Abstract
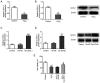
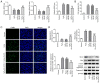
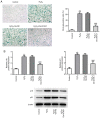
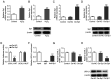
Age-related hearing loss (ARHL) is the most common cause of hearing loss in the elderly. Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCHL1) is a deubiquitinating enzyme involved in several types of human disease. The present study aimed to investigate the effect of UCHL1 on a hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced ARHL model in cochlear hair cells and uncover its underlying mechanism. Reverse transcription-quantitative (RT-q)PCR and western blot analysis were used to assess UCHL1 expression in HEI-OC1 cells exposed to H2O2. Following UCHL1 overexpression in H2O2-induced HEI-OC1 cells, cell activity was assessed by Cell Counting Kit-8 assay. The content of oxidative stress-associated markers including superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) and reactive oxygen species (ROS ) was measured using corresponding commercial kits. Cell apoptosis was evaluated by TUNEL assay and western blot analysis. Cell senescence was assessed by senescence-associated β-galactosidase staining and western blot analysis. RT-qPCR and western blot analysis were applied to measure mRNA and protein expression levels, respectively, of specificity protein 1 (Sp1) in H2O2-treated HEI-OC1 cells. In addition, the association between UCHL1 and Sp1 was verified by luciferase reporter and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay. The mRNA and protein expression levels of UCHL1 were also determined in Sp1-overexpressing cells by RT-qPCR and western blot analysis, respectively. Following Sp1 overexpression in UCHL1-overexpressing H2O2-treated HEI-OC1 cells, cell activity, oxidative stress, apoptosis and senescence were assessed. Finally, the expression levels of NF-κB signaling-related proteins p-NF-κB p65 and NF-κB p65 were detected using western blot analysis. The results showed that UCHL1 was downregulated in H2O2-treated HEI-OC1 cells. In addition, UCHL1 overexpression enhanced cell viability and promoted oxidative damage, apoptosis and senescence in H2O2-induced HEI-OC1 cells. Furthermore, Sp1 was upregulated in H2O2-treated HEI-OC1 cells. Additionally, luciferase reporter and ChIP assays demonstrated that Sp1 interacted with the UCHL1 promoter to inhibit UCHL1 transcription. Sp1 overexpression reversed the effect of UCHL1 overexpression on cell viability, oxidative stress, apoptosis, senescence and activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway in H2O2-exposed HEI-OC1 cells. Collectively, the results suggested that UCHL1 transcriptional suppression by Sp1 protected cochlear hair cells from H2O2-triggered senescence and oxidative damage.
Keywords: age-related hearing loss; oxidative stress; senescence; specificity protein 1; ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase L1.
Copyright: © Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vitamin C ameliorates D-galactose-induced senescence in HEI-OC1 cells by inhibiting the ROS/NF-κB pathway.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Nov 15;51(1):1157. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-10098-3. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39546096
-
AIMP1 exerts hearing protection role in age related hearing loss mice by regulating SIRT1 expression.BMC Geriatr. 2025 Aug 20;25(1):645. doi: 10.1186/s12877-025-06237-5. BMC Geriatr. 2025. PMID: 40836274 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidation of the mechanism of miR-122-5p in mediating FOXO3 injury and apoptosis of mouse cochlear hair cells induced by hydrogen peroxide.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Jun;23(6):435. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11362. Epub 2022 May 9. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 35607378 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Hippo/YAP signaling pathway ameliorates cochlear hair cell injury by regulating ferroptosis.Tissue Cell. 2023 Jun;82:102051. doi: 10.1016/j.tice.2023.102051. Epub 2023 Feb 26. Tissue Cell. 2023. PMID: 36889225
-
Silencing of TXNIP attenuates oxidative stress injury in HEI-OC1 by inhibiting the activation of NLRP3 and NF-κB.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 10;10(18):e37753. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37753. eCollection 2024 Sep 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39381226 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Molecular Specializations Underlying Phenotypic Differences in Inner Ear Hair Cells of Zebrafish and Mice.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 26:2024.05.24.595729. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.24.595729. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Front Neurol. 2024 Oct 17;15:1437558. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1437558. PMID: 38826418 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Bioinformatics approach reveals the critical role of inflammation-related genes in age-related hearing loss.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 21;15(1):2687. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-83428-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39837906 Free PMC article.
-
OSBPL2 inhibition leads to apoptosis of cochlea hair cells in age-related hearing loss by inhibiting the AKT/FOXG1 signaling pathway.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Oct 30;16(20):13132-13144. doi: 10.18632/aging.206138. Epub 2024 Oct 30. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 39475791 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin Ameliorates Senescence of Mouse Auditory Cell Line HEI-OC1 Cells by Suppressing NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Pyroptosis.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Aug;62(8):9902-9915. doi: 10.1007/s12035-025-04880-y. Epub 2025 Apr 2. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40169516 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular specializations underlying phenotypic differences in inner ear hair cells of zebrafish and mice.Front Neurol. 2024 Oct 17;15:1437558. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1437558. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39484049 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
