Chromosomes of parasitic wasps of the superfamily Chalcidoidea (Hymenoptera): An overview
- PMID: 36761105
- PMCID: PMC9849058
- DOI: 10.3897/CompCytogen.v14i3.56535
Chromosomes of parasitic wasps of the superfamily Chalcidoidea (Hymenoptera): An overview
Abstract
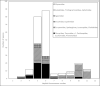
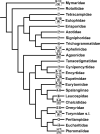
An overview of the current knowledge of chromosome sets of the parasitoid superfamily Chalcidoidea is given. Karyotypes of approximately 240 members of this group, i.e. just above one percent of described species, are studied up to now. Techniques for obtaining and analyzing preparations of chalcid chromosomes are outlined, including the so-called "traditional" and "modern" methods of differential staining as well as fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH). Among the Chalcidoidea, the haploid chromosome number can vary from n = 3 to n = 11, with a clear mode at n = 6 and a second local maximum at n = 10. In this group, most chromosomes are either metacentric or submetacentric, but acrocentrics and/or subtelocentrics also can predominate, especially within karyotypes of certain Chalcidoidea with higher chromosome numbers. The following main types of chromosomal mutations are characteristic of chalcid karyotypes: inversions, fusions, translocations, polyploidy, aneuploidy and B chromosome variation. Although karyotype evolution of this superfamily was mainly studied using phylogenetic reconstructions based on morphological and/or molecular characters, chromosomal synapomorphies of certain groups were also revealed. Taxonomic implications of karyotypic features of the Chalcidoidea are apparently the most important at the species level, especially among cryptic taxa.
Keywords: FISH; base-specific fluorochromes; chalcid wasps; differential staining; karyotypes; phylogeny; taxonomy.
Vladimir E. Gokhman.
Figures
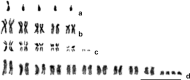
Similar articles
-
Comparative Karyotype Analysis of Parasitoid Hymenoptera (Insecta): Major Approaches, Techniques, and Results.Genes (Basel). 2022 Apr 25;13(5):751. doi: 10.3390/genes13050751. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35627136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A karyological study of the genus Pnigalio Schrank (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae): assessing the taxonomic utility of chromosomes at the species level.Bull Entomol Res. 2012 Feb;102(1):43-50. doi: 10.1017/S0007485311000356. Epub 2011 Jul 8. Bull Entomol Res. 2012. PMID: 21736855
-
Chromosomes of Pseudapantelesdignus (Muesebeck, 1938) and a review of known karyotypes of the subfamily Microgastrinae (Hymenoptera, Braconidae).Comp Cytogenet. 2024 Nov 21;18:199-211. doi: 10.3897/compcytogen.18.133534. eCollection 2024. Comp Cytogenet. 2024. PMID: 39619648 Free PMC article.
-
A cytogenetic study of three parasitic wasp species (Hymenoptera, Chalcidoidea, Eulophidae, Trichogrammatidae) from Brazil using chromosome morphometrics and base-specific fluorochrome staining.Comp Cytogenet. 2017 Mar 17;11(1):179-188. doi: 10.3897/CompCytogen.v11i1.11706. eCollection 2017. Comp Cytogenet. 2017. PMID: 28919957 Free PMC article.
-
Chromosome evolution in the Salmonidae (Pisces): an update.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2001 Feb;76(1):1-25. doi: 10.1017/s1464793100005613. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2001. PMID: 11325050 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular characterization of constitutive heterochromatin in three species of Trypoxylon (Hymenoptera: Crabronidae: Trypoxylini) by CMA3/DAPI staining.Comp Cytogenet. 2011 Jul 1;5(2):71-80. doi: 10.3897/compcytogen.v5i2.961. eCollection 2011. Comp Cytogenet. 2011. PMID: 24260620 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and Evolution of Ribosomal Genes of Insect Chromosomes.Insects. 2024 Aug 4;15(8):593. doi: 10.3390/insects15080593. Insects. 2024. PMID: 39194798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A reference genome for Trichogramma kaykai: A tiny desert-dwelling parasitoid wasp with competing sex-ratio distorters.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 23:2024.11.22.624848. doi: 10.1101/2024.11.22.624848. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: G3 (Bethesda). 2025 Aug 6;15(8):jkaf129. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkaf129. PMID: 39605481 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Comparative Karyotype Analysis of Parasitoid Hymenoptera (Insecta): Major Approaches, Techniques, and Results.Genes (Basel). 2022 Apr 25;13(5):751. doi: 10.3390/genes13050751. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35627136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
First description of the karyotype of a eucharitid wasp (Hymenoptera, Chalcidoidea, Eucharitidae).Comp Cytogenet. 2015 Sep 29;9(4):607-12. doi: 10.3897/CompCytogen.v9i4.5201. eCollection 2015. Comp Cytogenet. 2015. PMID: 26753077 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altinordu F, Peruzzi L, Yu Y, He X. (2016) A tool for the analysis of chromosomes: KaryoType. Taxon 65(3): 586–592. 10.12705/653.9 - DOI
-
- Baldanza F, Gaudio L, Viggiani G. (1999) Cytotaxonomic studies of Encarsia Förster (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae). Bulletin of Entomological Research 89: 209–215. 10.1017/S0007485399000322 - DOI
-
- Baldanza F, Giorgini M. (2001) Karyotype and NOR localization differences between Encarsiaformosa Gahan and Encarsialuteola Howard (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae). Bollettino del Laboratorio di Entomologia agraria ‘Filippo Silvestri’ 56: 33–41.
-
- Baur H, Kranz-Baltensperger Y, Cruaud A, Rasplus J-Y, Timokhov AV, Gokhman VE. (2014) Morphometric analysis and taxonomic revision of Anisopteromalus Ruschka (Hymenoptera: Chalcidoidea: Pteromalidae) – an integrative approach. Systematic Entomology 39: 691–709. 10.1111/syen.12081 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bolsheva NL, Gokhman VE, Muravenko OV, Gumovsky AV, Zelenin AV. (2012) Comparative cytogenetic study on two species of the genus Entedon Dalman, 1820 (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae) using DNA-binding fluorochromes and molecular and immunofluorescent markers. Comparative Cytogenetics 6(1): 79–92. 10.3897/compcytogen.v6i1.2349 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
