Predictors of weight loss in patients with obesity treated with a Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet
- PMID: 36761216
- PMCID: PMC9905243
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1058364
Predictors of weight loss in patients with obesity treated with a Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet
Abstract
Introduction: The Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD) has emerged as a safe and effective intervention for the management of metabolic disease. Studies examining weight loss predictors are scarce and none has investigated such factors upon VLCKD treatment. Among the molecules involved in energy homeostasis and, more specifically, in metabolic changes induced by ketogenic diets, Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 (FGF21) is a hepatokine with physiology that is still unclear.
Methods: We evaluated the impact of a VLCKD on weight loss and metabolic parameters and assessed weight loss predictors, including FGF21. VLCKD is a severely restricted diet (<800 Kcal/die), characterized by a very low carbohydrate intake (<50 g/day), 1.2-1.5 g protein/kg of ideal body weight and 15-30 g of fat/day. We treated 34 patients with obesity with a VLCKD for 45 days. Anthropometric parameters, body composition, and blood and urine chemistry were measured before and after treatment.
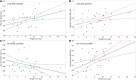
Results: We found a significant improvement in body weight and composition and most metabolic parameters. Circulating FGF21 decreased significantly after the VLCKD [194.0 (137.6-284.6) to 167.8 (90.9-281.5) p < 0.001] and greater weight loss was predicted by lower baseline FGF21 (Beta = -0.410; p = 0.012), male sex (Beta = 0.472; p = 0.011), and central obesity (Beta = 0.481; p = 0.005).
Discussion: VLCKD is a safe and effective treatment for obesity and obesity related metabolic derangements. Men with central obesity and lower circulating FGF21 may benefit more than others in terms of weight loss obtained following this diet. Further studies investigating whether this is specific to this diet or to any caloric restriction are warranted.
Keywords: body composition; fibroblast growth factor 21; insulin resistance; low carbohydrate diet (LCD); protein sparing modified fasting; very low energy diet.
Copyright © 2023 Ernesti, Baratta, Watanabe, Risi, Camajani, Persichetti, Tuccinardi, Mariani, Lubrano, Genco, Spera, Gnessi and Basciani.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Baseline HOMA IR and Circulating FGF21 Levels Predict NAFLD Improvement in Patients Undergoing a Low Carbohydrate Dietary Intervention for Weight Loss: A Prospective Observational Pilot Study.Nutrients. 2020 Jul 18;12(7):2141. doi: 10.3390/nu12072141. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32708435 Free PMC article.
-
Chronotype as a predictor of weight loss and body composition improvements in women with overweight or obesity undergoing a very low-calorie ketogenic diet (VLCKD).Clin Nutr. 2023 Jul;42(7):1106-1114. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2023.05.014. Epub 2023 May 19. Clin Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37236871
-
A very-low-calorie ketogenic diet normalises obesity-related enhanced levels of erythropoietin compared with a low-calorie diet or bariatric surgery.J Endocrinol Invest. 2024 Nov;47(11):2701-2713. doi: 10.1007/s40618-024-02364-9. Epub 2024 May 2. J Endocrinol Invest. 2024. PMID: 38696124 Free PMC article.
-
European Guidelines for Obesity Management in Adults with a Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Obes Facts. 2021;14(2):222-245. doi: 10.1159/000515381. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Obes Facts. 2021. PMID: 33882506 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of a Very-Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet in the Gut Microbiota Composition in Obesity.Nutrients. 2023 Jun 13;15(12):2728. doi: 10.3390/nu15122728. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37375632 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
FGF21 mediating the Sex-dependent Response to Dietary Macronutrients.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2024 Aug 13;109(9):e1689-e1696. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgae363. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2024. PMID: 38801670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ketogenic diets are associated with an elevated risk of hypertension: Insights from a cross-sectional analysis of the NHANES 2007-2018.Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Risk Prev. 2024 Oct 10;23:200342. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcrp.2024.200342. eCollection 2024 Dec. Int J Cardiol Cardiovasc Risk Prev. 2024. PMID: 39484088 Free PMC article.
-
Does a Ketogenic Diet Have a Place Within Diabetes Clinical Practice? Review of Current Evidence and Controversies.Diabetes Ther. 2024 Jan;15(1):77-97. doi: 10.1007/s13300-023-01492-4. Epub 2023 Nov 15. Diabetes Ther. 2024. PMID: 37966583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 in Chronic Hepatitis C: A Potential Non-Invasive Biomarker of Liver Status upon Viral Eradication.Metabolites. 2023 Oct 30;13(11):1119. doi: 10.3390/metabo13111119. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37999215 Free PMC article.
-
Very Low Calorie Ketogenic Diet: What Effects on Lipid Metabolism?Curr Nutr Rep. 2024 Sep;13(3):516-526. doi: 10.1007/s13668-024-00556-6. Epub 2024 Jul 15. Curr Nutr Rep. 2024. PMID: 39008211 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Castellana M, Conte E, Cignarelli A, Perrini S, Giustina A, Giovanella L, et al. Efficacy and safety of very low calorie ketogenic diet (VLCKD) in patients with overweight and obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. (2020) 21:5–16. 10.1007/s11154-019-09514-y - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

