Impact of Metacognition on Health-Related Behavior: A Mediation Model Study
- PMID: 36761241
- PMCID: PMC9904901
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/6547804
Impact of Metacognition on Health-Related Behavior: A Mediation Model Study
Abstract
Objective: The study aims to explore the correlation mechanism among metacognition, attitude toward physical exercise, and health-related behavior in high school students.
Methods: A total of 869 students (17 ± 1.70) from Anhui, Zhejiang, Shandong, and Fujian provinces were selected by stratified sampling to complete the Metacognition Questionnaire, Health-Related Behavior Self-Rating Scale, Attitude Toward Physical Exercise Scale, and Depression-Anxiety-Stress Scale (Simplified Chinese version, DASS-21).
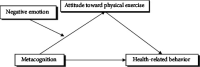
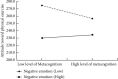
Results: (1) Metacognition was negatively predictive of attitude toward physical exercise and health-related behavior (β = -0.236, P < 0.01; β = -0.239, P < 0.01) but positively predictive of negative emotion (β = 0.496, P < 0.01); (2) attitude toward physical exercise was positively predictive of health-related behavior (β = 0.533, P < 0.01) but negatively predictive of negative emotion (β = -0.336, P < 0.01); and (3) negative emotion was negatively predictive of health-related behavior (β = -0.389, P < 0.01).
Conclusions: Metacognition not only has a directly predictive effect on health-related behavior but also predicts it through attitude toward physical exercise. Negative emotion also mediates the relationship between metacognition and attitude toward physical exercise.
Copyright © 2023 Yue Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Council T. S. Notice of the general office of the State Council on printing and distributing the national health plan for the 14th five year plan. Bulletin of the State Council of the people’s Republic of China . 2022;23(16):17–31.
-
- Lastrucci V., Lazzeretti M., Innocenti F., et al. Trends in adolescent health risk behaviors and wellbeing: a 10 Year observation from the edit surveillance of tuscany region, Italy. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health . 2022;19(11):p. 6863. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19116863. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources