Occupational Disease and Injury in Malaysia: A Thematic Review of Literature from 2016 to 2021
- PMID: 36761248
- PMCID: PMC9904905
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/1798434
Occupational Disease and Injury in Malaysia: A Thematic Review of Literature from 2016 to 2021
Abstract
Introduction: Working people are exposed to occupational hazards and are at risk of having occupational disease or injury in a rapidly industrializing country like Malaysia. This study aims to review and summarize the occupational disease and injury in Malaysia from 2016 to 2021.
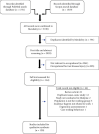
Methods: This study used PubMed and Scopus databases to conduct a systematic literature search using a set of keywords. The selected records dated from 1 January 2016 to 8 September 2021 were extracted into the Mendeley Desktop and ATLAS.ti 8 software. Systematic screening was conducted by two independent researchers and finalized by the third researcher. Data were coded and grouped according to the themes. The results were presented as the table for descriptive analysis and cross-tabulation between the themes.
Results: A total of 120 records were included in this study. Under the theme of main health problems, the findings showed that mental health, infectious disease, and work-related musculoskeletal disorders are the top three problems being discussed in the literature for the working people in Malaysia. The findings also showed an increasing trend of mental health problems during pandemic COVID-19 years. In addition, hospital was the highest workplace where the occupational health problems were reported.Discussion/Conclusion. There was substantial work on the mental health problem, infectious diseases, and work-related musculoskeletal disorders as the main health problem among workers in Malaysia in the past five years. The employers must report any occupational health and injury case to the authority and prompt intervention can be initiated.
Copyright © 2023 S. Maria Awaluddin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wolf J., Prüss-Ustün A., Ivanov I. Preventing Disease through a Healthier and Safer Workplace . Shandong Province, China: 2018.
-
- Pega F., Hamzaoui H., Náfrádi B., Momen N. C. Global, regional and national burden of disease attributable to 19 selected occupational risk factors for 183 countries, 2000–2016: a systematic analysis from the WHO/ILO Joint Estimates of the Work-related Burden of Disease and Injury. Scandinavian Journal of Work, Environment & Health . 2022;48(2):158–168. doi: 10.5271/sjweh.4001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Protecting workers’ health. 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous