Assessment of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients' behavioral characteristics associated with integrated treatment and prevention services in community health centers in China
- PMID: 36761334
- PMCID: PMC9905244
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1084946
Assessment of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients' behavioral characteristics associated with integrated treatment and prevention services in community health centers in China
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of this study was to describe behavioral characteristics of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients, identify homogeneous clusters, and explore factors affecting behaviors associated with integrated treatment and prevention (ITP) services for T2DM in community health centers in China.
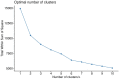
Methods: A convenient sampling method was employed at a community health center between January and July 2022 in Nanjing. A total of 354 patients completed the self-reported questionnaires. After performing a Cluster Analysis to create a profile of participants' behaviors, a multiple linear regression analysis was conducted to explore the correlations between T2DM patients' characteristics and their behaviors associated with ITP services.
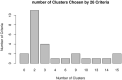
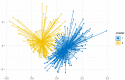
Results: 316 T2DM patients with a mean age of 72.09 years (SD = 5.96) were included. The behavior profiles of patients associated with ITP services were clustered into "Lower" (n = 198) and "Higher" (n = 118) groups, with average scores of 54.41 and 71.46, respectively. Of all the behaviors, complication examination and public health utilization scored the lowest. Health insurance, duration of disease, and treatment modality were independent predictors on the patients' behaviors associated with ITP services for T2DM.
Conclusion: Patients' behaviors associated with ITP services for T2DM were moderately good (the score rate was 63.98%). Of all the behaviors, complication examination and public health service utilization scored the lowest and, as such, may warrant further research. The clustering of patients' behaviors tends to be polarization, distributed at the upper and lower ends of the behavior spectrum. It is necessary to develop and implement targeted interventions for different groups to improve T2DM patients' behaviors associated with ITP services.
Keywords: behavior; cluster analysis; integrated treatment and prevention; multiple linear regression analysis; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Copyright © 2023 Zhao, Zhao, Wang, Zhang, Ding, Li, Miao, Pan and Fan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Global diabetes data report 2000–2045 . Available online at: https://diabetesatlas.org/data/ (accessed December 13, 2022).
-
- GBD, Results . Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. Available online at: https://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-results (accessed December 12, 2022).
-
- Diabetes prevalence (% of population ages 20 to 79)|Data . Available online at: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/SH.STA.DIAB.ZS (accessed December 13, 2022).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

