Competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) networks in Parkinson's disease: A systematic review
- PMID: 36761351
- PMCID: PMC9902725
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1044634
Competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) networks in Parkinson's disease: A systematic review
Abstract
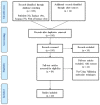
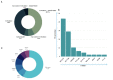
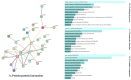
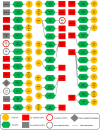
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a distinctive clinical syndrome with several causes and clinical manifestations. Aside from an infectious cause, PD is a rapidly developing neurological disorder with a global rise in frequency. Notably, improved knowledge of molecular pathways and the developing novel diagnostic methods may result in better therapy for PD patients. In this regard, the amount of research on ceRNA axes is rising, highlighting the importance of these axes in PD. CeRNAs are transcripts that cross-regulate one another via competition for shared microRNAs (miRNAs). These transcripts may be either coding RNAs (mRNAs) or non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). This research used a systematic review to assess validated loops of ceRNA in PD. The Prisma guideline was used to conduct this systematic review, which entailed systematically examining the articles of seven databases. Out of 309 entries, forty articles met all criteria for inclusion and were summarized in the appropriate table. CeRNA axes have been described through one of the shared vital components of the axes, including lncRNAs such as NEAT1, SNHG family, HOTAIR, MALAT1, XIST, circRNAs, and lincRNAs. Understanding the multiple aspects of this regulatory structure may aid in elucidating the unknown causal causes of PD and providing innovative molecular therapeutic targets and medical fields.
Keywords: NEAT1; Parkinson's disease; SNHG; ceRNA; circRNA; lincRNA; lncRNA; miRNA.
Copyright © 2023 Asadi, Abed, Kouchakali, Fattahi, Sabaie, Moslehian, Sharifi-Bonab, Hussen, Taheri, Ghafouri-Fard and Rezazadeh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identifying a Comprehensive ceRNA Network to Reveal Novel Targets for the Pathogenesis of Parkinson's Disease.Front Neurol. 2020 Aug 4;11:810. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00810. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32849243 Free PMC article.
-
The Traces of Dysregulated lncRNAs-Associated ceRNA Axes in Retinoblastoma: A Systematic Scope Review.Curr Eye Res. 2024 Jun;49(6):551-564. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2024.2306859. Epub 2024 Feb 1. Curr Eye Res. 2024. PMID: 38299506
-
CircRNA-Associated CeRNAs Regulatory Axes in Retinoblastoma: A Systematic Scoping Review.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 5;12:910470. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.910470. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35865469 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Insight Into the Therapeutic Potential of Long Non-coding RNA-Associated Competing Endogenous RNA Axes in Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Scoping Review.Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Nov 25;13:742242. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.742242. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34899268 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome Sequencing of lncRNAs, circRNAs, miRNAs, mRNAs, and Interaction Network Constructing in Acute Exacerbation of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Discov Med. 2023 Oct;35(178):887-896. doi: 10.24976/Discov.Med.202335178.84. Discov Med. 2023. PMID: 37811627
Cited by
-
Roles of HOTAIR Long Non-coding RNA in Gliomas and Other CNS Disorders.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Feb 16;44(1):23. doi: 10.1007/s10571-024-01455-8. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38366205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bibliometric analysis of microRNAs and Parkinson's disease from 2014 to 2023.Front Neurol. 2024 Sep 25;15:1466186. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1466186. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39385824 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis of plasma and substantia nigra in Parkinson's disease: unraveling biomarkers and insights from the lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA network.Front Aging Neurosci. 2024 May 9;16:1388655. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1388655. eCollection 2024. Front Aging Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38784444 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated bioinformatics analysis for exploring potential biomarkers related to Parkinson's disease progression.BMC Med Genomics. 2024 May 17;17(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s12920-024-01885-9. BMC Med Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38760670 Free PMC article.
-
Screening, identification, and experimental validation of SUMOylation biomarkers in Parkinson's disease.Hereditas. 2025 Aug 8;162(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s41065-025-00525-1. Hereditas. 2025. PMID: 40781725 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amin N., McGrath A., Chen Y.-P. P. (2019). Evaluation of deep learning in non-coding RNA classification. Nat. Mach. Intell. 1, 246–256. 10.1038/s42256-019-0051-2 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

