The pharmacokinetic and residue depletion study of eugenol in carp (Cyprinus carpio)
- PMID: 36761404
- PMCID: PMC9905725
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1097812
The pharmacokinetic and residue depletion study of eugenol in carp (Cyprinus carpio)
Abstract
Introduction: The pharmacokinetic profile and residue depletion of eugenol in carp (Cyprinus carpio) tissues and plasma were performed by a convenient and reliable high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method.
Methods: The eugenol in carp tissues and plasma was extracted with a mixed solution of acetonitrile and methanol. N-hexane was used to remove lipid impurities. The method was successfully applied to the pharmacokinetic and residue elimination of eugenol in carp after the carp was administered a medicated bath.
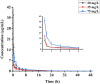
Results: The average recoveries of eugenol in tissues and plasma fortified with four concentration levels were 69.0-106.6% and 80.0-86.7%, respectively. The relative standard deviations were < 8.9%. The limit of detection (LOD) was 0.01 μg/g in tissue and 0.008 μg/ml in plasma, respectively. The pharmacokinetic parameter of Cmax for eugenol in plasma at the concentrations of 20, 35, and 75 mg/L were 10.86, 17.21, and 37.32 mg/L, respectively. The t1/2 values were 3.68, 4.22, and 9.31 h. After the investigation of the anesthetic effect, 35 mg/L of eugenol was the optimal concentration for anesthesia. The highest accumulation concentration of eugenol in carp is in the liver and the lowest is in the muscle. In addition, the eugenol in tissue was eliminated rapidly and at a lower level than the LOD at 48 h. According to the residue elimination, the withdrawal time of eugenol was suggested at 5.2 days.
Discussion: These results indicate that the developed method had good linearity and accuracy, and is sensitive enough for the monitoring of eugenol residue in carp. The half-life of eugenol decreased with the increase in drug concentration and the eugenol was eliminated rapidly in carp tissues. 35 mg/L eugenol was recommended as an anesthetic in carp due to its favorable anesthetic effect and no mortality. This study will contribute to the establishment of MRL regulation and setting a withdrawal period.
Keywords: carp; depletion; eugenol; high performance liquid chromatography; pharmacokinetic.
Copyright © 2023 Xu, Jiao, Yang, Tan, Ou, Song and Lv.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Elimination kinetics of eugenol in grass carp in a simulated transportation setting.BMC Vet Res. 2017 Nov 21;13(1):346. doi: 10.1186/s12917-017-1273-3. BMC Vet Res. 2017. PMID: 29162104 Free PMC article.
-
Temperature-dependent pharmacokinetics of trichlorfon in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) after bath immersion therapy.J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Sep;44(5):820-828. doi: 10.1111/jvp.12978. Epub 2021 May 10. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33973248
-
Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Residue Profiles of Enrofloxacin in Crucian Carp (Carassius auratus gibelio) Following Single and Multiple Oral Administration.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Apr 14;9:872828. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.872828. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35498735 Free PMC article.
-
Florfenicol pharmacokinetics following intravenous and oral administrations and its elimination after oral and bath administrations in common carp (Cyprinus carpio).Vet Res Forum. 2017;8(4):327-331. Epub 2017 Dec 15. Vet Res Forum. 2017. PMID: 29326792 Free PMC article.
-
Bioaccumulation of metals in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) from water bodies of Anatolia (Turkey): a review with implications for fisheries and human food consumption.Environ Monit Assess. 2016 Apr;188(4):243. doi: 10.1007/s10661-016-5248-9. Epub 2016 Mar 23. Environ Monit Assess. 2016. PMID: 27007291 Review.
Cited by
-
Residual depletion of eugenol as an anesthetic in growing phase pacu (Piaractus mesopotamicus).Vet Res Commun. 2025 Apr 17;49(3):168. doi: 10.1007/s11259-025-10739-3. Vet Res Commun. 2025. PMID: 40244480
-
Tissue distribution of Ocimum basilicum essential oil in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus after anesthesia.Vet Res Commun. 2025 Mar 21;49(3):148. doi: 10.1007/s11259-025-10716-w. Vet Res Commun. 2025. PMID: 40113623
-
Eugenol: An Insight Into the Anticancer Perspective and Pharmacological Aspects.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Aug 3;13(8):e70727. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70727. eCollection 2025 Aug. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40761498 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Khalil AA, Rahman UU, Khan MR, Sahar A, Mehmood T, Khan M. Essential oil eugenol: sources, extraction techniques and nutraceutical perspectives. RSC Adv. (2017) 7:32669–81. 10.1039/C7RA04803C - DOI
-
- Tago A, Yokoyama S, Ishikawa M, Koshio S. Pharmacokinetics of eugenol in Japanese flounder, paralichthys olivaceus. J World Aquac Soc. (2018) 49:780–7. 10.1111/jwas.12438 - DOI
-
- Pattanasiri T, Taparhudee W, Suppakul P. Acute toxicity and anaesthetic effect of clove oil and eugenol on siamese fighting fish, betta splendens. Aquaculture Int. (2017) 25:163–75. 10.1007/s10499-016-0020-2 - DOI
-
- Eman Z, Engy R, Awad R. Comparison propofol and eugenol anesthetics efficacy and effects on general health in Nile tilapia. Aquaculture. (2021) 534:736251. 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.736251 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

