The Effect of Social Appearance Anxiety on the Online Impulse Purchases of Fashionable Outfits Among Female College Students During Pandemic Periods: The Mediating Role of Self-Control and the Moderating Role of Subjective Socioeconomic Status
- PMID: 36761413
- PMCID: PMC9904223
- DOI: 10.2147/PRBM.S392414
The Effect of Social Appearance Anxiety on the Online Impulse Purchases of Fashionable Outfits Among Female College Students During Pandemic Periods: The Mediating Role of Self-Control and the Moderating Role of Subjective Socioeconomic Status
Abstract
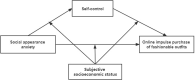
Purpose: With the rise of social media, an increasing number of young females have focused more attention on their body image, leading to social appearance anxiety. Thus, the current study aimed to investigate a moderated mediation model of social appearance anxiety and online impulse purchases of fashionable outfits through self-control moderated by subjective socioeconomic status during the pandemic.
Methods: A total of 1651 female college students (Age = 17-24, Mage = 19.30, SD = 1.14) with more than one month of closed-off management experience completed self-report questionnaires concerning social appearance anxiety, self-control, online impulse purchases of fashionable outfits, and subjective socioeconomic status.
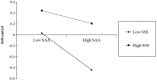
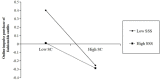
Results: After controlling for the potential influence of coronavirus stress, the results indicated that social appearance anxiety was positively related to online impulse purchases of fashionable outfits among female college students during the pandemic, mediated by self-control. Furthermore, subjective socioeconomic status moderated the indirect link between social appearance anxiety and the online impulse purchase of fashionable outfits. Specifically, subjective socioeconomic status buffers the negative effect of social appearance anxiety on self-control and the risk effect of low self-control on the online impulse purchases of fashionable outfits.
Implications: The current study deepens the research on the relationship between social appearance anxiety and online impulse purchases during pandemic periods; meanwhile, it provides evidence for preventing excessive online impulse purchases of fashionable outfits among young females.
Keywords: fashionable outfits; online impulse purchases; pandemic periods; self-control; social appearance anxiety; subjective socioeconomic status.
© 2023 Xiao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- NHCC. Transcript of the press conference of the joint defense and control mechanism of the State Council on March 25; 2022. Available from: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/xcs/yqfkdt/202203/7ae455e5e5db4512a471ab4f9500e8e7.... Accessed March 25, 2022.
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Situation Report. World Health Organization; 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources