Real-life analysis of neoadjuvant-therapy-associated benefits for pathological complete response and survival in early breast cancer patients - role of trastuzumab in HER2+ BC and platinum in TNBC
- PMID: 36761415
- PMCID: PMC9902925
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1022994
Real-life analysis of neoadjuvant-therapy-associated benefits for pathological complete response and survival in early breast cancer patients - role of trastuzumab in HER2+ BC and platinum in TNBC
Abstract
Background: Neoadjuvant therapy, which aims to achieve a pathological complete response (pCR) for better overall survival (OS) has several advantages for patients with early breast cancer (eBC) and subtypes of HER2-positive (HER2+) and triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). However, there has been no large-scale real-world investigation on the clinical outcomes associated with trastuzumab-based and platinum-based neoadjuvant treatments for patients with HER2+ and TNBC, respectively.
Material and methods: Taiwan Cancer Registry and National Health Insurance Research Database were utilized in this study. Patients diagnosed with clinically lymph-node-positive (LN+) HER2+ or TNBC were identified for analysis. Logistic regression and Cox proportional hazard models were employed to estimate the adjusted odds ratios (aOR) of achieving pCR and adjusted hazard ratios (aHR) of overall survival associated with treatment agents, respectively.
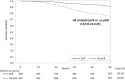
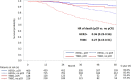
Results: A total of 1,178 HER2+ eBC and 354 early TNBC patients were identified, respectively. Neoadjuvant trastuzumab significantly increased the pCR rates by 3.87-fold among HER2+ patients. Trastuzumab-associated survival benefit was found in HER2+ patients who achieved pCR (aHR [95% CI]: 0.30 [0.11-0.84]) but not in those without pCR (1.13 [0.77-1.67]). Among the TNBC patients, platinum was associated with a 1.6-fold increased pCR rate; however, it did not improve OS regardless of pCR status.
Conclusions: Trastuzumab improved pCR and OS for patients with HER2+ subtype. Using platinum agents for TNBC patients increased pCR rates but was not linked to better survival. Optimal neoadjuvant anti-HER2 therapy for patients with HER2+ eBC and the introduction of novel therapy for patients with TNBC should be considered.
Keywords: HER2-positive breast cancer; early breast cancer; neoadjuvant therapy; platinum; trastuzumab; triple-negative breast cancer.
Copyright © 2023 Chung, Yang, Yang, Su, Su, Liu and Ou.
Conflict of interest statement
C-YS, H-WS, and S-YL are employees of Roche Products Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Impact of HER2-low status for patients with early-stage breast cancer and non-pCR after neoadjuvant chemotherapy: a National Cancer Database Analysis.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Feb;204(1):89-105. doi: 10.1007/s10549-023-07171-z. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 38066250
-
Differential response of triple-negative breast cancer to a docetaxel and carboplatin-based neoadjuvant treatment.Cancer. 2010 Sep 15;116(18):4227-37. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25309. Cancer. 2010. PMID: 20549829 Clinical Trial.
-
Neoadjuvant treatment and survival outcomes by pathologic complete response in HER2-negative early breast cancers.Future Oncol. 2023 Jan;19(3):229-244. doi: 10.2217/fon-2022-0801. Epub 2023 Mar 28. Future Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36974619
-
Neoadjuvant therapy for triple negative and HER2-positive early breast cancer.Breast. 2017 Aug;34 Suppl 1:S99-S103. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2017.06.038. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Breast. 2017. PMID: 28666920 Review.
-
Ki67 and lymphocytes in the pretherapeutic core biopsy of primary invasive breast cancer: positive markers of therapy response prediction and superior survival.Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2017 Sep 22;32(2):/j/hmbci.2017.32.issue-2/hmbci-2017-0022/hmbci-2017-0022.xml. doi: 10.1515/hmbci-2017-0022. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2017. PMID: 28937963 Review.
References
-
- Spring LM, Fell G, Arfe A, Sharma C, Greenup R, Reynolds KL, et al. . Pathologic complete response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and impact on breast cancer recurrence and survival: A comprehensive meta-analysis. Clin Cancer Res (2020) 26(12):2838–48. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-3492 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buzdar AU, Ibrahim NK, Francis D, Booser DJ, Thomas ES, Theriault RL, et al. . Significantly higher pathologic complete remission rate after neoadjuvant therapy with trastuzumab, paclitaxel, and epirubicin chemotherapy: results of a randomized trial in human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive operable breast cancer. J Clin Oncol (2005) 23(16):3676–85. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.07.032 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

