m7G-related gene NUDT4 as a novel biomarker promoting cancer cell proliferation in lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 36761423
- PMCID: PMC9902657
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1055605
m7G-related gene NUDT4 as a novel biomarker promoting cancer cell proliferation in lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: Lung cancer is the leading cause of mortality in cancer patients. N7-methylguanosine (m7G) modification as a translational regulation pattern has been reported to participate in multiple types of cancer progression, but little is known in lung cancer. This study attempts to explore the role of m7G-related proteins in genetic and epigenetic variations in lung adenocarcinoma, and its relationship with clinical prognosis, immune infiltration, and immunotherapy.
Methods: Sequencing data were obtained from the Genomic Data Commons (GDC) Data Portal and Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) databases. Consensus clustering was utilized to distinguish m7G clusters, and responses to immunotherapy were also evaluated. Moreover, univariate and multivariate Cox and Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator LASSO Cox regression analyses were used to screen independent prognostic factors and generated risk scores for constructing a survival prediction model. Multiple cell types such as epithelial cells and immune cells were identified to verify the bulk RNA results. Short hairpin RNA (shRNA) Tet-on plasmids, Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats CRISPR/Cas9 for knockout plasmids, and nucleoside diphosphate linked to moiety X-type motif 4 (NUDT4) overexpression plasmids were constructed to inhibit or promote tumor cell NUDT4 expression, then RT-qPCR, Cell Counting Kit-8 CCK8 proliferation assay, and Transwell assay were used to observe tumor cell biological functions.
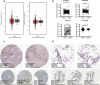
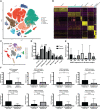
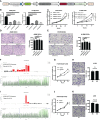
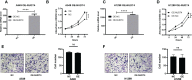
Results: Fifteen m7G-related genes were highly expressed in tumor samples, and 12 genes were associated with poor prognosis. m7G cluster-B had lower immune infiltration level, worse survival, and samples that predicted poor responses to immunotherapy. The multivariate Cox model showed that NUDT4 and WDR4 (WD repeat domain 4) were independent risk factors. Single-cell m7G gene set variation analysis (GSVA) scores also had a negative correlation tendency with immune infiltration level and T-cell Programmed Death-1 PD-1 expression, but the statistics were not significant. Knocking down and knocking out the NUDT4 expression significantly inhibited cell proliferation capability in A549 and H1299 cells. In contrast, overexpressing NUDT4 promoted tumor cell proliferation. However, there was no difference in migration capability in the knockdown, knockout, or overexpression groups.
Conclusions: Our study revealed that m7G modification-related proteins are closely related to the tumor microenvironment, immune cell infiltration, responses to immunotherapy, and patients' prognosis in lung adenocarcinoma and could be useful biomarkers for the identification of patients who could benefit from immunotherapy. The m7G modification protein NUDT4 may be a novel biomarker in promoting the progression of lung cancer.
Keywords: N7-methylguanosine modification; NUDT4; immune infiltration; immunotherapy; lung adenocarcinoma; prognosis.
Copyright © 2023 Liu, Jiang, Lin, Zhu, Chen, Sheng, Lou, Ji, Wu and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Construction of m7G RNA modification-related prognostic model and prediction of immune therapy response in hepatocellular carcinoma.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Jun 30;13(6):2799-2811. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-22. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38988942 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a diagnostic model utilizing m7G regulatory factors for the characterization of diabetic nephropathy and the immune microenvironment.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 17;15(1):9208. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-93811-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40097518 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting prognosis and immune responses in hepatocellular carcinoma based on N7-methylguanosine-related long noncoding RNAs.Front Genet. 2022 Aug 30;13:930446. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.930446. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36110218 Free PMC article.
-
N7-methylguanosine modification: from regulatory roles to therapeutic implications in cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 May 15;13(5):1640-1655. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37293166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
M7G-related tumor immunity: novel insights of RNA modification and potential therapeutic targets.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Jan 27;20(4):1238-1255. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.90382. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38385078 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A novel study on CXXC5: unraveling its regulatory mechanisms in hematopoietic stem cell biology through proteomics and gene editing.Genes Genomics. 2024 Oct;46(10):1133-1147. doi: 10.1007/s13258-024-01540-8. Epub 2024 Aug 16. Genes Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39150611
-
Selection of M7G-related lncRNAs in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma and their putative diagnostic and prognostic role.BMC Urol. 2023 Nov 15;23(1):186. doi: 10.1186/s12894-023-01357-9. BMC Urol. 2023. PMID: 37968670 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the tumor immune microenvironment of lung adenocarcinoma using single-cell RNA sequencing.Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2024 Apr 10;16:17588359231210274. doi: 10.1177/17588359231210274. eCollection 2024. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38606165 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of current developments in RNA modifications in lung cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Oct 25;24(1):347. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03528-6. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 39456034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploration and validation of m7G-related genes as signatures in the immune microenvironment and prognostic indicators in low-grade glioma.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Jun 15;15(6):3882-3899. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 37434820 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kerpel-Fronius A, Monostori Z, Kovacs G, Ostoros G, Horvath I, Solymosi D, et al. . Nationwide lung cancer screening with low-dose computed tomography: Implementation and first results of the HUNCHEST screening program. Eur Radiol (2022) 32(7):4457-4467. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-08589-7 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yotsukura M, Asamura H, Motoi N, Kashima J, Yoshida Y, Nakagawa K, et al. . Long-term prognosis of patients with resected adenocarcinoma In situ and minimally invasive adenocarcinoma of the lung. J Thorac Oncol Off Publ Int Assoc Study Lung Cancer. (2021) 16(8):1312–20. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2021.04.007 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Isomoto K, Haratani K, Hayashi H, Shimizu S, Tomida S, Niwa T, et al. . Impact of EGFR-TKI treatment on the tumor immune microenvironment in mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res an Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res (2020) 26(8):2037–46. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-2027 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

