Development and optimization of nanoparticles loaded with erucin, a dietary isothiocyanate isolated from Eruca sativa: Antioxidant and antiproliferative activities in ehrlich-ascites carcinoma cell line
- PMID: 36761468
- PMCID: PMC9905727
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1080977
Development and optimization of nanoparticles loaded with erucin, a dietary isothiocyanate isolated from Eruca sativa: Antioxidant and antiproliferative activities in ehrlich-ascites carcinoma cell line
Abstract
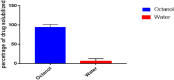
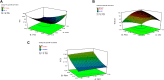
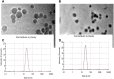
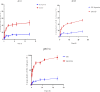
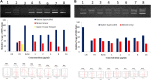
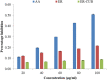
The study on Erucin (ER) has gained interest of nutraceutical and pharmaceutical industries because of its anti-cancer properties. Erucin is an isothiocyanate obtained from the seeds of Eruca sativa which possess certain drawbacks such as poor aqueous solubility and bioavailability. Therefore, the present study aimed at developing ER-cubosomes (CUB) by solvent evaporation technique followed by applying Central Composite Design to optimize ER loaded cubosomes. For this purpose, independent variables selected were Monoolein (MO) as lipid and Pluronic-84 (P-84) as a stabilizer whereas dependent variables were particle size, percentage of ER loading and percentage of its entrapment efficiency. The cubosomal nanocarriers exhibited particle size in the range of 26 nm, entrapment efficiency of 99.12 ± 0.04% and drug loading of 3.96 ± 0.0001%. Furthermore, to investigate the antioxidant potential, we checked the effect of ER and ER-CUB by DNA nicking assay, DDPH assay and Phosphomolybdate assay, and results showed significant improvement in antioxidant potential for ER-CUB than ER. Similarly, ER-CUB showed enhanced anticancer activity with a marked reduction in IC50 value than ER in MTT assay. These results suggested that ER-CUB produced notable escalation in antioxidant potential and enhanced anticancer activity than ER.
Keywords: antioxidant assay; central composite design; colon cancer; cubosomes; ehrlich ascites carcinoma; erucin.
Copyright © 2023 Singh, Singh, Attri, Kaur, Rashid, Bedi, Haque, Janahi and Arora.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Attri S., Kaur P., Singh D., Kaur H., Rashid F., Kumar A., et al. (2022). Induction of apoptosis in A431 cells via ROS generation and p53-mediated pathway by chloroform fraction of Argemone mexicana (Pepaveraceae). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29, 17189–17208. 10.1007/s11356-021-16696-z - DOI - PubMed
-
- Awadelkareem A. M., Al-shammari E., Elkhalifa A. E. O., Adnan M., Patel M., Ashraf S. A. (2022a). Phytochemical and in silico ADME/tox analysis of Eruca sativa extract with antioxidant, antibacterial and anticancer potential against caco-2 and HCT-116 colorectal carcinoma cell lines. Molecules 27, 1409. 10.3390/molecules27041409 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Awadelkareem A. M., Al-shammari E., Elkhalifa A. E. O., Adnan M., Danciu C., Ashraf S. A. (2022b). Anti-adhesion and antibiofilm activity of Eruca sativa miller extract targeting cell adhesion proteins of food-borne bacteria as a potential mechanism: Combined in vitro-in slico approach. Plants 11, 610. 10.3390/plants11050610 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

