Visualization analysis of thoracic paravertebral block in breast surgery based on bibliometrics
- PMID: 36761487
- PMCID: PMC9906098
- DOI: 10.21037/gs-22-754
Visualization analysis of thoracic paravertebral block in breast surgery based on bibliometrics
Abstract
Background: Breast surgery is one of the most common surgeries in the world, and pain after breast surgery is very common, representing one of the key factors affecting the quality of life after surgery. With the development of clinical techniques, thoracic paravertebral block (TPVB) has gradually become the preferred regional anesthesia technique for postoperative breast analgesia.
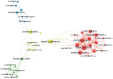
Methods: Using Web of Science as the data source, medical articles about the application of TPVB in breast surgery published from 1900 to 2022 were retrieved and imported into CiteSpace and VOSviewer software. Using bibliometrics and knowledge mapping visualization methods, the literature was analyzed from the aspects of publication, author, institution, country, high-frequency keywords, keyword clustering, emergence words, and so on.
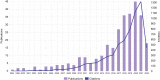
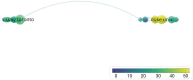
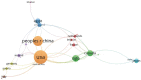
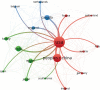
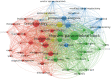
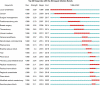
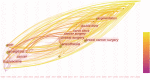
Results: A total of 299 articles were included. according to the yearly numbers of articles, the trend is increasing annually. The most published authors in this field are Susan M. Steele, Roy A. Greengrass, Brian M. Ilfeld, Karmakar Manoj Kumar, and Stephen M. Klein. The League of European Research Universities, University of Toronto, and Duke University are the 3 institutions with the largest number of publications, and their cooperation degree is relatively low. Articles of American origin predominated. TPVB is the major keyword associated with the application of TPVB in breast surgery, which appears most frequently and has a high research interest.
Conclusions: The trend and characteristics of TPVB application research in breast surgery were visualized, and the studies in this field are generally increasing annually in number, providing useful bibliometric analysis for researchers to further explore in this field.
Keywords: Thoracic paravertebral block (TPVB); bibliometric; breast surgery.
2023 Gland Surgery. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://gs.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/gs-22-754/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
