Quantitative fluorescence resonance energy transfer-based immunoassay for activated complement C1s
- PMID: 36761732
- PMCID: PMC9904206
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1081793
Quantitative fluorescence resonance energy transfer-based immunoassay for activated complement C1s
Abstract
Objectives: C1s activation is associated with the pathogenesis of various diseases, indicating the potential value of C1s activation detection in clinic. Here we aimed to establish fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based immunoassay for the quantitative detection of activated C1s in serum.
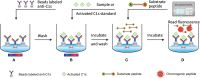
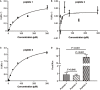
Methods: FRET-based fluorogenic peptides, sensitive to the enzymatic activity of activated C1s, were prepared and labeled with the fluorophore ortho-aminobenzoic acid (Abz) and quencher 2,4-dinitrophenyl (Dnp), and then were further selected depending on its Kcat/Km value. C1s in the samples was captured and separated using anti-C1s-conjugated magnetic microbeads. Next, enzymatic activity of activated C1s in samples and standards was examined using fluorescent quenched substrate assays. Limit of detection (LOD), accuracy, precision, and specificity of FRET-based immunoassay were also investigated.
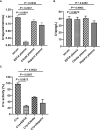
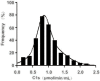
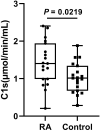
Results: This method presented a linear quantification range for the enzymatic activity of activated C1s up to 10 μmol min-1 mL-1 and LOD of 0.096 μmol·min-1·mL-1 for serum samples. The recovery of the method was in the range of 90% ~ 110%. All CV values of the intra-analysis and inter-analysis of three levels in samples were less than 10%. The cross-reaction rates with C1r enzyme, MASP1, and MASP2 were less than 0.5%. No significant interferences were found with bilirubin (0.2 mg mL-1), Chyle (2000 FTU), and haemoglobin (5 mg mL-1), but anticoagulants (EDTA, citrate and heparin) inhibited the enzymatic ability of activated C1s. Thus, this established method can be used for the determination of active C1s in human serum samples in the concentration interval of 0.096-10.000 μmol min-1 mL-1.
Conclusions: One anti-C1s-based FRET immunoassay for activated C1s detection in serum samples were established, and it will be useful to explore the role of C1s activation in the pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment in complement-related diseases.
Keywords: C1s; C2; C4; FRET; complement; immunoassay.
Copyright © 2023 Ye, Xu, Zhang, Zhu and Xia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MASP1 (MBL-associated serine protease 1).Immunobiology. 1998 Aug;199(2):340-7. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(98)80038-7. Immunobiology. 1998. PMID: 9777417 Review.
-
Trimer and tetramer complexes containing C1 esterase inhibitor, C1r and C1s, in serum and synovial fluid of patients with rheumatic disease.J Immunol Methods. 1990 May 8;129(1):55-61. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90420-z. J Immunol Methods. 1990. PMID: 2338498
-
C1 activation and dissociation in disease.Immunol Lett. 1987 Feb;14(3):249-53. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(87)90109-x. Immunol Lett. 1987. PMID: 3032782
-
Recombinant human complement subcomponent C1s lacking beta-hydroxyasparagine, sialic acid, and one of its two carbohydrate chains still reassembles with C1q and C1r to form a functional C1 complex.Biochemistry. 1992 May 5;31(17):4254-62. doi: 10.1021/bi00132a015. Biochemistry. 1992. PMID: 1533159
-
Complement C1s as a diagnostic marker and therapeutic target: Progress and propective.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 6;13:1015128. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1015128. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36275687 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

