Kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies in Omicron breakthrough cases with inactivated vaccination: Role in inferring the history and duration of infection
- PMID: 36761738
- PMCID: PMC9902649
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1083523
Kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies in Omicron breakthrough cases with inactivated vaccination: Role in inferring the history and duration of infection
Abstract
Background: The quantitative level and kinetics of neutralizing antibodies (NAbs) in individuals with Omicron breakthrough infections may differ from those of vaccinated individuals without infection. Therefore, we aimed to evaluate the difference in NAb levels to distinguish the breakthrough cases from the post-immunized population to identify early infected person in an outbreak epidemic when nasal and/or pharyngeal swab nucleic acid real-time PCR results were negative.
Methods: We collected 1077 serum samples from 877 individuals, including 189 with Omicron BA.2 breakthrough infection and 688 post-immunized participants. NAb titers were detected using the surrogate virus neutralization test, and were log(2)-transformed to normalize prior to analysis using Student's unpaired t-tests. Geometric mean titers (GMT) were calculated with 95% confidence intervals (CI). Linear regression models were used to identify factors associated with NAb levels. We further conducted ROC curve analysis to evaluate the NAbs' ability to identify breakthrough infected individuals in the vaccinated population.
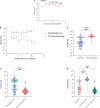
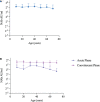
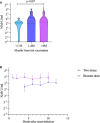
Results: The breakthrough infection group had a consistently higher NAb levels than the post-immunized group according to time since the last vaccination. NAb titers in the breakthrough infection group were 6.4-fold higher than those in the post-immunized group (GMT: 40.72 AU/mL and 6.38 AU/mL, respectively; p<0.0001). In the breakthrough infection group, the NAbs in the convalescent phase were 10.9-fold higher than in the acute phase (GMT: 200.48 AU/mL and 18.46 AU/mL, respectively; p<0.0001). In addition, the time since infection, booster vaccination, and the time since last vaccination were associated with log(2)-transformed NAb levels in the breakthrough infection group. ROC curve analysis showed that ROC area was largest (0.728) when the cut-off value of log(2)-transformed NAb was 6, which indicated that NAb levels could identify breakthrough infected individuals in the vaccinated population.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrates that the NAb titers of Omicron BA.2 variant breakthrough cases are higher than in the post-immunized group. The difference in NAb levels could be used to identify cases of breakthrough infection from the post-immunized population in an outbreak epidemic.
Keywords: Omicron variant; SARS-CoV-2; breakthrough infection; inactive CoronaVac; neutralizing antibody.
Copyright © 2023 Simayi, Li, Chen, Wang, Dong, Tian, Kong, Zhou, Peng, Zhang, Zhu, Hu, Xu, Jin, Fan, Bao and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of vaccination on kinetics of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 by serum live neutralization test based on a prospective cohort.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2023 Dec;12(1):2146535. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2022.2146535. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2023. PMID: 36373485 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Responses up to 9 Months Post-Vaccination in Individuals with Previous SARS-CoV-2 Infection Receiving Inactivated Vaccines.Viruses. 2023 Apr 4;15(4):917. doi: 10.3390/v15040917. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37112897 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling a New Perspective on Distinguishing Omicron Breakthrough Cases and Postimmune COVID-19-Naive Individuals: Insights from Antibody Profiles.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Aug 17;11(4):e0180823. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01808-23. Epub 2023 Jul 11. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37432106 Free PMC article.
-
Boosting of serum neutralizing activity against the Omicron variant among recovered COVID-19 patients by BNT162b2 and CoronaVac vaccines.EBioMedicine. 2022 May;79:103986. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.103986. Epub 2022 Apr 8. EBioMedicine. 2022. PMID: 35398786 Free PMC article.
-
Infection-mediated immune response in SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infection and implications for next-generation COVID-19 vaccine development.Vaccine. 2024 Feb 27;42(6):1401-1406. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2024.01.088. Epub 2024 Feb 2. Vaccine. 2024. PMID: 38310015 Review.
Cited by
-
Low levels of neutralizing antibodies against XBB Omicron subvariants after BA.5 infection.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Jun 19;8(1):252. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01495-4. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37336889 Free PMC article.
-
A recombinant protein vaccine induces protective immunity against SARS-CoV-2 JN.1 and XBB-lineage subvariants.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Feb 26;10(1):58. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02154-6. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 40000611 Free PMC article.
-
Role of senescent CD4+ T cells in breakthrough infection of the new variant strain of SARS-CoV-2 in elderly patients.J Transl Med. 2025 Jul 3;23(1):737. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06756-0. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40611132 Free PMC article.
-
The serological IgG and neutralizing antibody of SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant reinfection in Jiangsu Province, China.Front Public Health. 2024 May 30;12:1364048. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1364048. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38873290 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . When you’ve been fully vaccinated. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/fully-vaccinated.html (Accessed 8 November 2021).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

