Skin-associated adipocytes in skin barrier immunity: A mini-review
- PMID: 36761769
- PMCID: PMC9902365
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1116548
Skin-associated adipocytes in skin barrier immunity: A mini-review
Abstract
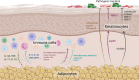
The skin contributes critically to health via its role as a barrier tissue against a multitude of external pathogens. The barrier function of the skin largely depends on the uppermost epidermal layer which is reinforced by skin barrier immunity. The integrity and effectiveness of skin barrier immunity strongly depends on the close interplay and communication between immune cells and the skin environment. Skin-associated adipocytes have been recognized to play a significant role in modulating skin immune responses and infection by secreting cytokines, adipokines, and antimicrobial peptides. This review summarizes the recent understanding of the interactions between skin-associated adipocytes and other skin cells in maintaining the integrity and effectiveness of skin barrier immunity.
Keywords: adipocytes; adipokines; antimicrobial peptides; infection; skin barrier immunity.
Copyright © 2023 Guan, Wu, He and Lu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources