The neutrophil elastase inhibitor, sivelestat, attenuates acute lung injury in patients with cardiopulmonary bypass
- PMID: 36761773
- PMCID: PMC9902923
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1082830
The neutrophil elastase inhibitor, sivelestat, attenuates acute lung injury in patients with cardiopulmonary bypass
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: The neutrophil elastase inhibitor, Sivelestat, attenuates acute lung injury in patients with cardiopulmonary bypass.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 1;14:1165081. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1165081. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36936938 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: The sivelestat is a neutrophil elastase inhibitor thought to have an effect against acute lung injury (ALI) in patients after scheduled cardiac surgery. However, the beneficial effect of sivelestat in patients undergoing emergent cardiovascular surgery remains unclear. We aim to evaluate the effect of sivelestat on pulmonary protection in patients with ALI after emergent cardiovascular surgery.
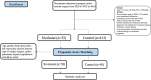
Methods: Firstly, a case-control study in 665 patients undergoing emergent cardiovascular surgery from January 1st, 2020 to October 26th, 2022 was performed. 52 patients who received sivelestat (0.2mg/kg/h for 3 days) and 613 age- and sex-matched controls. Secondly, a propensity-score matched cohort (sivelestat vs control: 50 vs 50) was performed in these 665 patients. The primary outcome was a composite of adverse outcomes, including 30-day mortality, ECMO, continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) and IABP, etc. The secondary outcome included pneumonia, ventricular arrhythmias and mechanical ventilation time, etc.
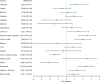
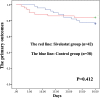
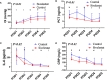
Results: In propensity-matched patients, the 30-day mortality (16% vs 24%, P=0.32), stroke (2% vs 8%, P=0.17), ECMO(6% vs 10%, P=0.46), IABP(4% vs 8%, P=0.40) and CRRT(8% vs 20%, P=0.08) had no differences between sivelestat and control group; sivelestat could significantly decrease pneumonia (40% vs 62%, P=0.03), mechanical ventilation time (median: 96hours, IQR:72-120hours vs median:148hours, IQR:110-186hours, P<0.01), bilateral pulmonary infiltrates (P<0.01), oxygen index (P<0.01), interleukin-6(P=0.02), procalcitonin(P<0.01) and C-reactive protein(P<0.01).
Conclusion: Administration of sivelestat might improve postoperative outcomes in patients with ALI after emergent cardiovascular surgery. Our results show that sivelestat may be considered to protect pulmonary function against inflammatory injury by CPB.
Registration: http://www.chictr.org.cn/showproj.aspx?proj=166643, identifier ChiCTR2200059102.
Keywords: acute lung injury; cardiopulmonary bypass; cardiovascular surgery; outcomes; sivelestat.
Copyright © 2023 Pan, Tuoerxun, Chen, Yang, Jiang, Zhu, Li, Jiang, Zhang, Zhang, Wang, Chen, Lu, Ge, Cheng, Wang and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sivelestat in Patients at a High Risk of Postoperative Acute Lung Injury After Scheduled Cardiac Surgery: A Prospective Cohort Study.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Feb 1;17:591-601. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S442208. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38318242 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of a neutrophil elastase inhibitor on acute lung injury after cardiopulmonary bypass.Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2010 Jun;10(6):859-62. doi: 10.1510/icvts.2009.225243. Epub 2010 Mar 30. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2010. PMID: 20354035 Clinical Trial.
-
Neutrophil elastase inhibitor sivelestat attenuates perioperative inflammatory response in pediatric heart surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass.Int Heart J. 2013;54(3):149-53. doi: 10.1536/ihj.54.149. Int Heart J. 2013. PMID: 23774238 Clinical Trial.
-
Neutrophil elastase inhibitor (sivelestat) may be a promising therapeutic option for management of acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome or disseminated intravascular coagulation in COVID-19.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2020 Dec;45(6):1515-1519. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13251. Epub 2020 Aug 28. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2020. PMID: 32860252 Review.
-
Clinical utility of the neutrophil elastase inhibitor sivelestat for the treatment of acute respiratory distress syndrome.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2014 Aug 5;10:621-9. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S65066. eCollection 2014. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2014. PMID: 25120368 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dual Roles of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1 in Acute Lung Injury: Tissue-Specific Mechanisms and Therapeutic Modulation.Cells. 2025 Jul 16;14(14):1089. doi: 10.3390/cells14141089. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40710342 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Neutrophil Elastase Inhibitor (Sivelestat Sodium) on Oxygenation in Patients with Sepsis-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Mar 27;18:4449-4458. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S506549. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40166593 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical severity classes in COVID-19 pneumonia have distinct immunological profiles, facilitating risk stratification by machine learning.Front Immunol. 2023 Sep 5;14:1192765. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1192765. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37731491 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophils and Platelets as Key Players in the Pathogenesis of ANCA-Associated Vasculitis and Potential Sources of Disease Activity Biomarkers.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Jul 29;15(15):1905. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15151905. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40804869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sivelestat (Neutrophil Elastase Inhibitor) as an Anti-inflammatory and Anti-viral Agent: An In Silico Study.Cureus. 2024 Mar 24;16(3):e56846. doi: 10.7759/cureus.56846. eCollection 2024 Mar. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38659558 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boyle EM, Jr, Pohlman TH, Johnson MC, Verrier ED. Endothelial cell injury in cardiovascular surgery: The systemic inflammatory response. Ann Thorac Surg (1997) 63:277–84. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

