Inflammasome activation by Gram-positive bacteria: Mechanisms of activation and regulation
- PMID: 36761775
- PMCID: PMC9902775
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1075834
Inflammasome activation by Gram-positive bacteria: Mechanisms of activation and regulation
Abstract
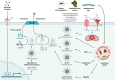
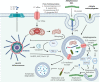
The inflammasomes are intracellular multimeric protein complexes consisting of an innate immune sensor, the adapter protein ASC and the inflammatory caspases-1 and/or -11 and are important for the host defense against pathogens. Activaton of the receptor leads to formation of the inflammasomes and subsequent processing and activation of caspase-1 that cleaves the proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-18. Active caspase-1, and in some instances caspase-11, cleaves gasdermin D that translocates to the cell membrane where it forms pores resulting in the cell death program called pyroptosis. Inflammasomes can detect a range of microbial ligands through direct interaction or indirectly through diverse cellular processes including changes in ion fluxes, production of reactive oxygen species and disruption of various host cell functions. In this review, we will focus on the NLRP3, NLRP6, NLRC4 and AIM2 inflammasomes and how they are activated and regulated during infections with Gram-positive bacteria, including Staphylococcus spp., Streptococcus spp. and Listeria monocytogenes.
Keywords: Gram-positive bacteria; autophagy; inflammasome; mechanisms of activation; regulation.
Copyright © 2023 Keestra-Gounder and Nagao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cytokine Secretion and Pyroptosis of Thyroid Follicular Cells Mediated by Enhanced NLRP3, NLRP1, NLRC4, and AIM2 Inflammasomes Are Associated With Autoimmune Thyroiditis.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 4;9:1197. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01197. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29915579 Free PMC article.
-
Pyroptosis in Antiviral Immunity.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2023;442:65-83. doi: 10.1007/82_2019_189. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2023. PMID: 31875268 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical role of ASC inflammasomes and bacterial type IV secretion system in caspase-1 activation and host innate resistance to Brucella abortus infection.J Immunol. 2013 Apr 1;190(7):3629-38. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202817. Epub 2013 Mar 4. J Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23460746
-
Inflammasomes as polyvalent cell death platforms.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Jun;73(11-12):2335-47. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2204-3. Epub 2016 Apr 5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 27048821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Inflammatory bowel diseases and inflammasome].Korean J Gastroenterol. 2011 Dec;58(6):300-10. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2011.58.6.300. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 22198227 Review. Korean.
Cited by
-
Interplay between group A Streptococcus and host innate immune responses.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2024 Mar 27;88(1):e0005222. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.00052-22. Epub 2024 Mar 7. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38451081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Episymbiotic Saccharibacteria suppresses epithelial immunoactivation through Type IV pili and TLR2 dependent endocytosis.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 2:2025.05.30.656655. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.30.656655. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40501963 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
The role of inflammasome in chronic viral hepatitis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 May 16;14:1382029. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1382029. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38817443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammasome and pyroptosis in autoimmune liver diseases.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 8;14:1150879. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1150879. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36969233 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunotherapy in mastitis: state of knowledge, research gaps and way forward.Vet Q. 2024 Dec;44(1):1-23. doi: 10.1080/01652176.2024.2363626. Epub 2024 Jul 7. Vet Q. 2024. PMID: 38973225 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

