Potential targeted therapy based on deep insight into the relationship between the pulmonary microbiota and immune regulation in lung fibrosis
- PMID: 36761779
- PMCID: PMC9904240
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1032355
Potential targeted therapy based on deep insight into the relationship between the pulmonary microbiota and immune regulation in lung fibrosis
Abstract
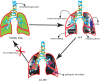
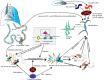
Pulmonary fibrosis is an irreversible disease, and its mechanism is unclear. The lung is a vital organ connecting the respiratory tract and the outside world. The changes in lung microbiota affect the progress of lung fibrosis. The latest research showed that lung microbiota differs in healthy people, including idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and acute exacerbation-idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (AE-IPF). How to regulate the lung microbiota and whether the potential regulatory mechanism can become a necessary targeted treatment of IPF are unclear. Some studies showed that immune response and lung microbiota balance and maintain lung homeostasis. However, unbalanced lung homeostasis stimulates the immune response. The subsequent biological effects are closely related to lung fibrosis. Core fucosylation (CF), a significant protein functional modification, affects the lung microbiota. CF regulates immune protein modifications by regulating key inflammatory factors and signaling pathways generated after immune response. The treatment of immune regulation, such as antibiotic treatment, vitamin D supplementation, and exosome micro-RNAs, has achieved an initial effect in clearing the inflammatory storm induced by an immune response. Based on the above, the highlight of this review is clarifying the relationship between pulmonary microbiota and immune regulation and identifying the correlation between the two, the impact on pulmonary fibrosis, and potential therapeutic targets.
Keywords: IPF – idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; immune regulation; lung fibrosis; lung microbiota; microecology.
Copyright © 2023 Zhang, Zhang, Yang, Gao and Sun.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Topographic heterogeneity of lung microbiota in end-stage idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: the Microbiome in Lung Explants-2 (MiLEs-2) study.Thorax. 2021 Mar;76(3):239-247. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2020-214770. Epub 2020 Dec 2. Thorax. 2021. PMID: 33268457 Free PMC article.
-
The Lung Microbiome in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Promising Approach for Targeted Therapies.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Dec 16;18(12):2735. doi: 10.3390/ijms18122735. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29258183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A phase II trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of perioperative pirfenidone for prevention of acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in lung cancer patients undergoing pulmonary resection: West Japan Oncology Group 6711 L (PEOPLE Study).Respir Res. 2016 Jul 22;17(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s12931-016-0398-4. Respir Res. 2016. PMID: 27450274 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Regulation of the IGF1 signaling pathway is involved in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis induced by alveolar epithelial cell senescence and core fucosylation.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Jul 30;13(14):18852-18869. doi: 10.18632/aging.203335. Epub 2021 Jul 30. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34329195 Free PMC article.
-
The contribution of infection and the respiratory microbiome in acute exacerbations of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Eur Respir Rev. 2019 Jul 8;28(152):190045. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0045-2019. Print 2019 Jun 30. Eur Respir Rev. 2019. PMID: 31285290 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metagenomic Analysis of Lung Microbiome in Patients With Interstitial Lung Diseases and Sarcoidosis: An Experimental Study.Health Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 6;8(2):e70328. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70328. eCollection 2025 Feb. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39927182 Free PMC article.
-
Update of Aging Hallmarks in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Cells. 2025 Feb 5;14(3):222. doi: 10.3390/cells14030222. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39937013 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lung microbiota: implications and interactions in chronic pulmonary diseases.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Aug 19;14:1401448. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1401448. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39233908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression and predictive value of serum core fucosylated low molecular weight kininogen and alpha-galactosylated antibodies in patients with hepatic fibrosis.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Jun 28;49(6):903-913. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2024.240018. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 39311786 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Predictive value of core-fucosylated low-molecular-weight kininogen levels in patients with liver fibrosis: A prospective study.World J Gastroenterol. 2025 Aug 7;31(29):105210. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i29.105210. World J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40809923 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

