In-vitro evaluation of immunomodulatory activity of sulphation-modified total ginsenosides derivative-3
- PMID: 36761888
- PMCID: PMC9907730
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1068315
In-vitro evaluation of immunomodulatory activity of sulphation-modified total ginsenosides derivative-3
Abstract
Background: Ginseng has been used in biomedicine to prevent and treat decreased physical and mental capacities. Total ginsenosides (TG) from ginseng root which have antitumor and immune-enhancing properties, are the principal active components of Panax ginseng, while the sulphation-modified TG derivative-3 (SMTG-d3) was expected to enhance the anticancer activity in conventional medicinal treatments.
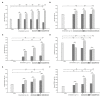
Methods: The chlorosulphonic acid-pyridine technique, used for the sulfation modification of TG to improve their biological activity, and the infrared spectroscopic characteristics of TG and SMTG-d3 were investigated, and the effects of SMTG-d3 on immunocytes and cytokines relevant to tumor treatment were assessed. The MTT assay was used to assess the effect of TG and SMTG-d3 on the cytotoxicity and T-lymphocytic proliferation against mouse splenocytes. The LDH method was employed to evaluate NK activity induced by TG or SMTG-d3. The production levels of splenocytes-secreted IL-2 and IFN-γ and peritoneal macrophages-secreted TNF-α were determined using mouse ELISA kits.
Results and discussion: It showed that the ideal conditions for the sulfation modification of TG: the volume ratio of chlorosulfonic acid to pyridine lower than 1:2.5; controlled amount of chlorosulfonic acid; and a yield of 51.5% SMTG-d3 (2 h, < 45°C). SMTG-d3 showed two characteristic absorption peaks at 1,230 cm-1 and 810 cm-1, indicating the formation of sulfuric acid esters and the presence of sulfuric acid groups. SMTG-d3 exhibited higher antitumor immunological activity than TG by promoting the proliferation of T lymphocytes and the production of IFN-γ and TNF-α, thus enhancing NK cell activity, and reducing cytotoxicity. The findings imply sulfated modification represents an effective method of enhancing the immunomodulatory activities of TG and could be used as the basis for developing new drug target compounds; SMTG-d3 can serve as an antitumor immunomodulator and can be considered an effective and prospective herbal formulation in clinical applications.
Keywords: antitumor; cytotoxicity; immunological activity; sulphation derivative; total ginsenosides (TG).
Copyright © 2023 Guo, Wang, Haq, Wang, Guo, Luo and Ijaz.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
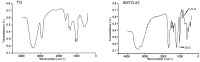
References
-
- Kiran K, Saleem F, Awan S, Ahmad S, Ahmad S, et al. . Anti-inflammatory and anticancer activity of pteris cretica whole plant extracts. Pak Vet J. (2018) 38:225–30. 10.29261/pakvetj/2018.063 - DOI
-
- Hussain Z, Khan JA, Arshad MI, Muhammad F, Abbas RZ. Protective effects of cinnamon, cinnamaldehyde and kaempferol against acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury and apoptosis in mouse model. Pak Vet J. (2021) 41:25–32. 10.29261/pakvetj/2020.090 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

