Krüppel-like factors in tumors: Key regulators and therapeutic avenues
- PMID: 36761967
- PMCID: PMC9905823
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1080720
Krüppel-like factors in tumors: Key regulators and therapeutic avenues
Abstract
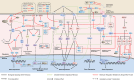
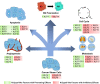
Krüppel-like factors (KLFs) are a group of DNA-binding transcriptional regulators with multiple essential functions in various cellular processes, including proliferation, migration, inflammation, and angiogenesis. The aberrant expression of KLFs is often found in tumor tissues and is essential for tumor development. At the molecular level, KLFs regulate multiple signaling pathways and mediate crosstalk among them. Some KLFs may also be molecular switches for specific biological signals, driving their transition from tumor suppressors to promoters. At the histological level, the abnormal expression of KLFs is closely associated with tumor cell stemness, proliferation, apoptosis, and alterations in the tumor microenvironment. Notably, the role of each KLF in tumors varies according to tumor type and different stages of tumor development rather than being invariant. In this review, we focus on the advances in the molecular biology of KLFs, particularly the regulations of several classical signaling pathways by these factors, and the critical role of KLFs in tumor development. We also highlight their strong potential as molecular targets in tumor therapy and suggest potential directions for clinical translational research.
Keywords: Krüppel-like factor; molecular target; signal transduction; tumor; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2023 Zhang, Yao, Ju, Jiao, Hu, Qi, Liu, Wu and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression and Function of Kruppel Like-Factors (KLF) in Carcinogenesis.Curr Genomics. 2009 Aug;10(5):353-60. doi: 10.2174/138920209788921010. Curr Genomics. 2009. PMID: 20119532 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging role of Krüppel-like factors in endocrine-responsive cancers of female reproductive tissues.J Endocrinol. 2010 Mar;204(3):223-31. doi: 10.1677/JOE-09-0329. Epub 2009 Oct 15. J Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 19833720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological and toxicological roles of Kruppel-like factors (KLFs) in the cardiovascular system: a review.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 May 26;52(1):506. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10613-0. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40418318 Review.
-
Modulation of Krüppel-like factors (KLFs) interaction with their binding partners in cancers through acetylation and phosphorylation.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2024 Mar;1867(1):195003. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2023.195003. Epub 2023 Nov 20. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2024. PMID: 37992989 Review.
-
Role of Krüppel-like factors in cancer stem cells.J Physiol Biochem. 2015 Mar;71(1):155-64. doi: 10.1007/s13105-015-0381-4. Epub 2015 Jan 24. J Physiol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25616500 Review.
Cited by
-
Abnormal expression of Krüppel-like transcription factors and their potential values in lung cancer.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 21;10(7):e28292. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28292. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38560274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transgenerational Transmission of 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) Effects in Human Granulosa Cells: The Role of MicroRNAs.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 17;25(2):1144. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021144. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38256218 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations of Krüppel-like Factor Signaling and Potential Targeted Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2025;25(2):75-85. doi: 10.2174/0118715206301453240910044913. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39313900 Review.
-
Krüppel-like Factor 10 as a Prognostic and Predictive Biomarker of Radiotherapy in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 30;15(21):5212. doi: 10.3390/cancers15215212. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37958386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integration of single-cell regulon atlas and multi-omics data for prognostic stratification and personalized treatment prediction in human lung adenocarcinoma.J Transl Med. 2023 Jul 25;21(1):499. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04331-z. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37491302 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

