Nutritional and lifestyle management of the aging journey: A narrative review
- PMID: 36761987
- PMCID: PMC9903079
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.1087505
Nutritional and lifestyle management of the aging journey: A narrative review
Abstract
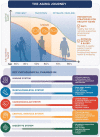
With age, the physiological responses to occasional or regular stressors from a broad range of functions tend to change and adjust at a different pace and restoring these functions in the normal healthy range becomes increasingly challenging. Even if this natural decline is somehow unavoidable, opportunities exist to slow down and attenuate the impact of advancing age on major physiological processes which, when weakened, constitute the hallmarks of aging. This narrative review revisits the current knowledge related to the aging process and its impact on key metabolic functions including immune, digestive, nervous, musculoskeletal, and cardiovascular functions; and revisits insights into the important biological targets that could inspire effective strategies to promote healthy aging.
Keywords: aging; lifestyle; metabolism; nutrition; physiological changes.
Copyright © 2023 Kassis, Fichot, Horcajada, Horstman, Duncan, Bergonzelli, Preitner, Zimmermann, Bosco, Vidal and Donato-Capel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that AK is a paid consultant to Société des Produits Nestlé and that all other authors are employees of Société des Produits Nestlé. The authors declare that this study received funding from Société des Produits Nestlé SA. The funder had the following involvement in this review article: review design, data collection, decision to publish and preparation of the manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- United Nations. World Population ageing 2019. Highlights. New York, NY: United Nations; (2019).
-
- GBD 2019 Demographics Collaborators. Global age-sex-specific fertility, mortality, healthy life expectancy (HALE), and population estimates in 204 countries and territories, 1950-2019: a comprehensive demographic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. (2020) 396:1160–203. 10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30977-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources