Conscious knowledge of CS-UCS contingency information affects extinction retrieval of conditioned disgust responses: Findings from an online de novo disgust conditioning task
- PMID: 36762035
- PMCID: PMC9883280
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijchp.2023.100368
Conscious knowledge of CS-UCS contingency information affects extinction retrieval of conditioned disgust responses: Findings from an online de novo disgust conditioning task
Abstract
Objective: The present study aimed to establish and develop an online de novo conditioning paradigm for the measurement of conditioned disgust responses. We further explored the effects of explicit instructions about the CS-UCS contingency on extinction learning and retrieval of conditioned disgust responses.
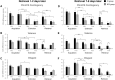
Method: The study included a sample of 115 healthy participants. Geometric figures served as conditioned stimuli (CS) and disgust-evoking pictures as unconditioned stimuli (UCS). During disgust conditioning, the CS+ was paired with the UCS (66% reinforcement) and the CS- remained unpaired; during extinction and retrieval, no UCS was presented. Half of the participants (n = 54) received instructions prior to the disgust extinction stating that the UCS will not be presented anymore. 1-2 days or 7-8 days later participants performed a retrieval test. CS-UCS contingency, disgust and valence ratings were used as dependent measures.
Results: Successful acquisition of conditioned disgust response was observed on the level of CS-UCS contingency, disgust and valence ratings. While some decline in valence and disgust ratings during the extinction stage was observed, contingency instructions did not significantly affect extinction performance. Retrieval one week later revealed that contingency instructions increased the discrimination of the CSs.
Conclusions: Extinction of conditioned disgust responses is not affected by explicit knowledge of the CS-UCS contingencies. However, contingency instructions prior to extinction seem to have a detrimental effect on long-term extinction retrieval.
Keywords: Awareness; Disgust; Extinction; Extinction retrieval; Instructions.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Blechert J., Michael T., Vriends N., Margraf J., Wilhelm F.H. Fear conditioning in posttraumatic stress disorder: Evidence for delayed extinction of autonomic, experiential, and behavioural responses. Behaviour Research and Therapy. 2007;45(9):2019–2033. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2007.02.012. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

