The association between clinical parameters and resectability in stage III non-small cell lung cancer, and a combination of N2 lymph node burden and lung immune prognostic index score as a potential biomarker
- PMID: 36762065
- PMCID: PMC9903093
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr-22-642
The association between clinical parameters and resectability in stage III non-small cell lung cancer, and a combination of N2 lymph node burden and lung immune prognostic index score as a potential biomarker
Abstract
Background: Surgery is important treatment option for stage III non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) because of its curative potential. We investigated the characteristics of resectable patients, and compared the outcomes according to treatment modalities.
Methods: Among 1,092 patients with NSCLC diagnosed between 2008 to 2020 from 7 university hospitals of Catholic Medical Center, we retrospectively analyzed 252 patients with clinical or pathological stage III. We compared survival outcomes among the groups according to resectability, first-line treatments, and the lung immune prognostic index (LIPI) score. Clinical N2 subgroup was analyzed using multi-parameter scoring system.
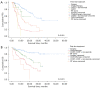
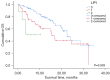
Results: The resectable group consisted of less smokers, showed better pulmonary function and lower inflammatory markers, and tended to be diagnosed as earlier cancer stage than the unresectable group. The resectable group showed better progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) than the unresectable group (P<0.001 and P<0.001, respectively). Regarding the first-line treatment, surgery showed the longest median PFS (33.70 months) and the highest 12-month OS rate (91.6%) than the other treatment modalities. OS was significantly different depending on the LIPI score in whole population, as well as in the unresectable group (P=0.004 and P=0.003, respectively). LIPI 0 group exhibited better OS than LIPI 1 and 2 in both populations. Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) 2-4, LIPI 1-2, and first-line treatment were independent prognostic factors for OS. Smoking, forced expiratory volume in the first second (FEV1) and more advanced cancer stage were associated with unresectability. In subgroup analysis of N2 disease, we attempted to create new scoring system combining lymph node (LN) status and LIPI score. This scoring system showed significant association with OS.
Conclusions: The patients with resectable stage III NSCLC showed better PFS and OS than the patients with unresectable tumor. LIPI score exhibited possibility to be used as potential biomarker in stage III NSCLC. The multi-parameter scoring system using LN status and LIPI score was predictive of OS in the N2 subgroup.
Keywords: Non-small-cell lung carcinoma; lung immune prognostic index (LIPI); overall survival (OS); progression-free survival (PFS); surgery.
2023 Translational Lung Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tlcr.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tlcr-22-642/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Correlation of Lung Immune Prognostic Index With Efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibitor Combined With Chemotherapy and Prognosis in Patients With Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Am J Clin Oncol. 2023 Nov 1;46(11):496-502. doi: 10.1097/COC.0000000000001035. Epub 2023 Aug 25. Am J Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37621004
-
Pretreatment lung immune prognostic index as a biomarker in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients receiving first line pembrolizumab.Immunotherapy. 2021 Sep;13(13):1093-1103. doi: 10.2217/imt-2021-0002. Epub 2021 Jun 30. Immunotherapy. 2021. PMID: 34190578
-
A validation study on the lung immune prognostic index for prognostic value in patients with locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Radiother Oncol. 2021 Mar;156:244-250. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2020.12.039. Epub 2021 Jan 5. Radiother Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33418003
-
Evaluation of the Lung Immune Prognostic Index in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated With Systemic Therapy: A Retrospective Study and Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2021 Jun 24;11:670230. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.670230. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34249708 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Inflammatory Markers of Survival in Epidermal Growth Factor-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Single-Institution Analysis, Systematic Review, and Meta-analysis.Clin Lung Cancer. 2021 Sep;22(5):390-407. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2021.01.002. Epub 2021 Jan 10. Clin Lung Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33582072
Cited by
-
Identifying optimal surgical approach among T1N2-3M0 non-small cell lung cancer patients: a population-based analysis.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024 Apr 29;13(4):901-929. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-213. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38736488 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
