Unraveling the effect of solvents on the excited state dynamics of C540A by experimental and theoretical study
- PMID: 36762085
- PMCID: PMC9906279
- DOI: 10.1039/d3ra00259d
Unraveling the effect of solvents on the excited state dynamics of C540A by experimental and theoretical study
Abstract
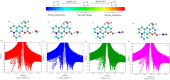
In this work, the excited-state dynamics including intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) and the redshift of C540A have been investigated in a series of solvents on the basis of the Kamlet-Taft solvatochromic parameters (π*, α, β) using femtosecond transient absorption spectra and systematic theoretical calculation. We demonstrate that the redshift of the emission peak has a linear relationship with the α and π* scales and the effect of the π* scale is slightly stronger than that of the α scale. Meanwhile, the ICT rates can be suggested as relevant to not only the α scale but also the π* scale. Additionally, C540A-AN has proved that the excited state molecules have a unique inactivation mechanism because of the dark feature of the S1 (CT) state. The valuable mechanistic information gleaned from the excited-state dynamics by the experimental and theoretical study would facilitate the design of organic materials for prospective applications in photochemistry and photobiology.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures


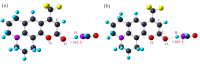


References
-
- Sugimoto K. Okubo T. Maekawa M. Kuroda-Sowa T. Cryst. Growth Des. 2021;21:4178–4183. doi: 10.1021/acs.cgd.1c00426. - DOI
-
- Zhang R. Ma S. H. Wei Q. B. Ye Q. Yu B. Van Der Gucht J. Zhou F. Macromolecules. 2015;48:6186–6196. doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.5b01267. - DOI
-
- Yamane H. Kosugi N. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2018;122:26472–26479. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b08346. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

