Displaced supracondylar femoral fractures: Clinical and radiographic outcomes in children aged 4-10 years treated with Kirschner wires and hip spica cast
- PMID: 36762282
- PMCID: PMC9902706
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2023.1086831
Displaced supracondylar femoral fractures: Clinical and radiographic outcomes in children aged 4-10 years treated with Kirschner wires and hip spica cast
Abstract
Background: Supracondylar femoral fractures (SFFs) are uncommon in children but can cause several abnormalities. Although several methods have been employed to treat these fractures, no accepted standard has been established.
Objectives: To investigate the clinical and radiographic outcomes of displaced SFFs treated with Kirschner wires (K-wires) and hip spica casts in children aged 4-10 years.
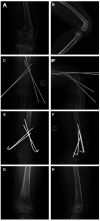
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 22 displaced SFFs (mean age, 6.7 years; range, 4-10 years) in patients who underwent surgical treatment with K-wires and hip spica casts. The patients were followed-up frequently, radiographically and clinically between January 2014 and February 2019. Postoperative healing and functional results were elevated according to the radiographic and clinical measures.
Results: Fifteen boys and seven girls were included in this study. All patients except two (91%), underwent closed reduction and stabilization of the fractures. The mean follow-up duration was four years (range, 2-5 years). All fractures showed clinical and radiological evidence of union 4-8 weeks after surgery. At the most recent check-up, all patients reported being pain-free and had returned to normal activities. The mean Knee Society Score was 95.41 at the final follow-up. According to the radiologic criteria, 18 of the 22 patients (81.8%) obtained excellent results, 3 (13.6%) had good results, 1 (4.5%) had a fair result, and none had poor results.
Conclusion: Satisfactory clinical and radiological results can be expected in children aged 4-10 years using a combination of K-wires and hip spica cast fixation.
Keywords: Kirschner wire; displaced; hip spica cast; pediatric; supracondylar femoral fractures.
© 2023 Jing, Ning, Mo and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

