The Abundance and Function of Neutrophils in the Endometriosis Systemic and Pelvic Microenvironment
- PMID: 36762287
- PMCID: PMC9904898
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/1481489
The Abundance and Function of Neutrophils in the Endometriosis Systemic and Pelvic Microenvironment
Abstract
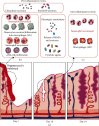
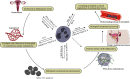
Endometriosis is a common inflammatory illness in which endometrial tissue grows outside the uterine cavity. Immune dysfunction is now widely acknowledged as the primary cause of endometriosis. The immune cell population represented by neutrophils is thought to play an essential role in the etiology, pathophysiology, and associated clinical outcome. There is growing evidence that neutrophils have a role in chronic and aseptic inflammatory diseases, and endometriosis patients have increased levels of neutrophils in plasma, peritoneal fluid, and ectopic endometrium. Here, we sought to review the function of neutrophils in the pathogenesis of endometriosis, with an emphasis on the role of neutrophils in regulating endometrial angiogenesis and the local inflammatory microenvironment.
Copyright © 2023 Xinlei Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Agarwal S. K., Chapron C., Giudice L. C., et al. Clinical diagnosis of endometriosis: a call to action. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology . 2019;220(354):e351–354.e312. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

