Multisequence magnetic resonance neurography of brachial and lumbosacral plexus in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: correlations with electrophysiological parameters and clinical features
- PMID: 36762318
- PMCID: PMC9905022
- DOI: 10.1177/17562864221150540
Multisequence magnetic resonance neurography of brachial and lumbosacral plexus in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: correlations with electrophysiological parameters and clinical features
Abstract
Background: Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) is a rare and challenging demyelinating disorder. It is necessary to increase our understanding of potential connections between imaging, electromyography, and clinical characteristics.
Objective: The aim of this study was to evaluate the relationships between multisequence magnetic resonance neurography (MRN) findings, electrophysiological parameters, and clinical characteristics in CIDP patients.
Design: A cross-sectional study.
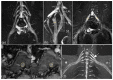
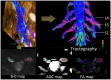
Methods: Overall, 51 CIDP patients underwent MRN of the brachial and lumbosacral plexus, and nerve conduction studies. The inflammatory Rasch-built overall disability scale (I-RODS) questionnaire, CIDP disease activity status (CADS) scale, and muscle strength scores were evaluated by two neurologists. Electrophysiological parameters, clinical information, and multiparameter-MRN were analyzed for correlations. Multiparameter-MRN includes diameter, nerve-to-muscle T2 signal intensity ratio (nT2), contrast-enhanced ratio (CR), fractional anisotropy (FA), and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) of bilateral plexus nerve roots.
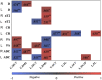
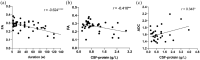
Results: Electrophysiological parameters that were not elicited were significantly higher in the lower extremities than in the upper extremities, and those were higher in sensory nerve conduction than in motor. There were moderate correlations between motor nerve conduction velocity and distal motor latency in nerve diameter, nT2, FA, and ADC, respectively (|r|, 0.45-0.64, p < 0.05). The correlations between CR and sensory nerve conduction velocity and peak latency were moderate, and ADC had a positive correlation with compound motor action potential amplitude (|r|, 0.45-0.63). FA correlated negatively with the course (r = -0.62) and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) protein (r = -0.41), whereas ADC had correlated positively with CSF protein (r = 0.34). Only CR had a moderately negative correlation with CADS (r's = -0.57). Muscle strength in all extremities was positively correlated with FA (r's range, 0.41-0.49). There was no significant correlation between I-RODS scores and multiparameter-MR.
Conclusion: MRN-derived multiparameter [nerve size, nT2, and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) parameters] could serve as quantitative biomarkers of myelin sheath integrity in CIDP. DTI parameters and CR correlated with clinical characteristics better than morphological parameters-MR for CIDP patients.
Keywords: chronic inflammatory demyelinating; diffusion tensor imaging; electrophysiology; magnetic resonance imaging; polyradiculoneuropathy.
© The Author(s), 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
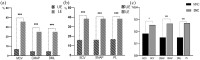
Similar articles
-
Multisequence Quantitative Magnetic Resonance Neurography of Brachial and Lumbosacral Plexus in Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy.Front Neurosci. 2021 Jul 23;15:649071. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.649071. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34366769 Free PMC article.
-
MR neurography of lumbosacral nerve roots: Diagnostic value in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy and correlation with electrophysiological parameters.Eur J Radiol. 2020 Mar;124:108816. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.108816. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Eur J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 31923808
-
Microstructural Alteration of Lumbosacral Nerve Roots in Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyradiculoneuropathy: Insights From DTI and Correlations with Electrophysiological Parameters.Acad Radiol. 2022 Mar;29 Suppl 3:S175-S182. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2021.08.006. Epub 2021 Oct 9. Acad Radiol. 2022. PMID: 34642113
-
The diagnostic value of quantitative assessment of MR neurography in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Br J Radiol. 2023 Nov;96(1151):20221037. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20221037. Epub 2023 Jul 4. Br J Radiol. 2023. PMID: 37393524 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative magnetic resonance (MR) neurography for evaluation of peripheral nerves and plexus injuries.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2017 Aug;7(4):398-421. doi: 10.21037/qims.2017.08.01. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2017. PMID: 28932698 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Semiquantitative assessment of preganglionic nerves for chronic immune-mediated neuropathies using brachial plexus magnetic resonance imaging.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 Apr 3;14(4):2968-2977. doi: 10.21037/qims-23-1473. Epub 2024 Mar 28. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 38617157 Free PMC article.
-
How much does clinical prediagnosis correlate with electrophysiological findings?: a retrospective study.J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2024 Jul;41(3):220-227. doi: 10.12701/jyms.2024.00381. Epub 2024 Jul 5. J Yeungnam Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38965681 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Latov N. Diagnosis and treatment of chronic acquired demyelinating polyneuropathies. Nat Rev Neurol 2014; 10: 435–446. - PubMed
-
- Rajabally YA, Stettner M, Kieseier BC, et al.. CIDP and other inflammatory neuropathies in diabetes – diagnosis and management. Nat Rev Neurol 2017; 13: 599–611. - PubMed
-
- Vallat JM, Sommer C, Magy L. Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: diagnostic and therapeutic challenges for a treatable condition. Lancet Neurol 2010; 9: 402–412. - PubMed
-
- Van den Bergh PYK, van Doorn PA, Hadden RDM, et al.. European Academy of Neurology/Peripheral Nerve Society guideline on diagnosis and treatment of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: report of a joint Task Force-Second revision. Eur J Neurol 2021; 28: 3556–3583. - PubMed
-
- van Nes SI, Vanhoutte EK, van Doorn PA, et al.. Rasch-built overall disability scale (R-ODS) for immune-mediated peripheral neuropathies. Neurology 2011; 76: 337–345. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

