Symptom Perceptions in Functional Disorders, Major Health Conditions, and Healthy Controls: A General Population Study
- PMID: 36762352
- PMCID: PMC9881122
- DOI: 10.32872/cpe.7739
Symptom Perceptions in Functional Disorders, Major Health Conditions, and Healthy Controls: A General Population Study
Abstract
Background: The present study investigated differences in symptom perceptions between individuals with functional disorders (FD), major health conditions, and FDs + major health conditions, respectively, and a group of healthy individuals. Furthermore, it investigated the relevance of FDs among other health-related and psychological correlates of symptom perceptions in the framework of the Common Sense Model of Self-Regulation (CMS).
Method: This cross-sectional study used epidemiological data from the Danish Study of Functional Disorders part two (N = 7,459 participants, 54% female, 51.99 ± 13.4 years). Symptom perceptions were assessed using the Brief Illness Perception Questionnaire (B-IPQ) and compared between the four health condition groups. Multiple regression analyses were performed to examine associations between symptom perceptions, FDs, and other health-related and psychological correlates from the CMS framework.
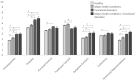
Results: Individuals with FDs (n = 976) and those with FDs + major health conditions (n = 162) reported less favorable symptom perceptions compared to the other two groups, particularly regarding perceived consequences, timeline, and emotional representations (effect size range Cohen's d = 0.12-0.66). The presence of a FD was significantly associated with all B-IPQ items, even in the context of 16 other relevant health-related and psychological correlates from the CMS framework, whereas symptom presence last year or last week was not.
Conclusion: In the general population, symptom perceptions seem to play a more salient role in FD than in individuals with well-defined physical illness. Symptom perceptions should therefore be targeted in both primary and secondary interventions for FDs.
Keywords: common-sense model of illness; epidemiological study; functional disorders; personality traits; quality of life; symptom perceptions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aalto, A.-M., Aro, A. R., Weinman, J., Heijmans, M., Manderbacka, K., & Elovainio, M. (2006). Sociodemographic, disease status, and illness perceptions predictors of global self-ratings of health and quality of life among those with coronary heart disease – One year follow-up study. Quality of Life Research, 15(8), 1307–1322. 10.1007/s11136-006-0010-3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anda, R. F., Felitti, V. J., Bremner, J. D., Walker, J. D., Whitfield, C., Perry, B. D., Dube, S. R., & Giles, W. H. (2006). The enduring effects of abuse and related adverse experiences in childhood: A convergence of evidence from neurobiology and epidemiology. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neuroscience, 256(3), 174–186. 10.1007/s00406-005-0624-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brace, M. J., Scott Smith, M., McCauley, E., & Sherry, D. D. (2000). Family reinforcement of illness behavior: A comparison of adolescents with chronic fatigue syndrome, juvenile arthritis, and healthy controls. Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics, 21(5), 332–339. 10.1097/00004703-200010000-00003 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
