Enabling Single-Cell Drug Response Annotations from Bulk RNA-Seq Using SCAD
- PMID: 36762572
- PMCID: PMC10104628
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202204113
Enabling Single-Cell Drug Response Annotations from Bulk RNA-Seq Using SCAD
Abstract
The single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) quantifies the gene expression of individual cells, while the bulk RNA sequencing (bulk RNA-seq) characterizes the mixed transcriptome of cells. The inference of drug sensitivities for individual cells can provide new insights to understand the mechanism of anti-cancer response heterogeneity and drug resistance at the cellular resolution. However, pharmacogenomic information related to their corresponding scRNA-Seq is often limited. Therefore, a transfer learning model is proposed to infer the drug sensitivities at single-cell level. This framework learns bulk transcriptome profiles and pharmacogenomics information from population cell lines in a large public dataset and transfers the knowledge to infer drug efficacy of individual cells. The results suggest that it is suitable to learn knowledge from pre-clinical cell lines to infer pre-existing cell subpopulations with different drug sensitivities prior to drug exposure. In addition, the model offers a new perspective on drug combinations. It is observed that drug-resistant subpopulation can be sensitive to other drugs (e.g., a subset of JHU006 is Vorinostat-resistant while Gefitinib-sensitive); such finding corroborates the previously reported drug combination (Gefitinib + Vorinostat) strategy in several cancer types. The identified drug sensitivity biomarkers reveal insights into the tumor heterogeneity and treatment at cellular resolution.
Keywords: drug response annotation; single-cell sequencing; transfer learning.
© 2023 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

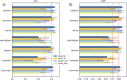

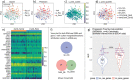

References
-
- McGranahan N., Swanton C., Cell 2017, 168, 613. - PubMed
-
- Wei W., Shin Y. S., Xue M., Matsutani T., Masui K., Yang H., Ikegami S., Gu Y., Herrmann K., Johnson D., Ding X., Hwang K., Kim J., Zhou J., Su Y., Li X., Bonetti B., Chopra R., James C. D., Cavenee W. K., Cloughesy T. F., Mischel P. S., Heath J. R., Gini B., Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 563. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
