Sp3 is essential for normal lung morphogenesis and cell cycle progression during mouse embryonic development
- PMID: 36762637
- PMCID: PMC10110423
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.200839
Sp3 is essential for normal lung morphogenesis and cell cycle progression during mouse embryonic development
Abstract
Members of the Sp family of transcription factors regulate gene expression via binding GC boxes within promoter regions. Unlike Sp1, which stimulates transcription, the closely related Sp3 can either repress or activate gene expression and is required for perinatal survival in mice. Here, we use RNA-seq and cellular phenotyping to show how Sp3 regulates murine fetal cell differentiation and proliferation. Homozygous Sp3-/- mice were smaller than wild-type and Sp+/- littermates, died soon after birth and had abnormal lung morphogenesis. RNA-seq of Sp3-/- fetal lung mesenchymal cells identified alterations in extracellular matrix production, developmental signaling pathways and myofibroblast/lipofibroblast differentiation. The lungs of Sp3-/- mice contained multiple structural defects, with abnormal endothelial cell morphology, lack of elastic fiber formation, and accumulation of lipid droplets within mesenchymal lipofibroblasts. Sp3-/- cells and mice also displayed cell cycle arrest, with accumulation in G0/G1 and reduced expression of numerous cell cycle regulators including Ccne1. These data detail the global impact of Sp3 on in vivo mouse gene expression and development.
Keywords: Alveolar development; Cell proliferation; Lipofibroblast; Lung mesenchyme; Myofibroblast; Transcriptional regulation.
© 2023. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures
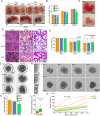




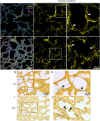


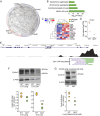
Similar articles
-
Sp1 trans-activation of cell cycle regulated promoters is selectively repressed by Sp3.Biochemistry. 1995 Dec 19;34(50):16503-8. doi: 10.1021/bi00050a034. Biochemistry. 1995. PMID: 8845379
-
Functional significance of Sp1, Sp2, and Sp3 transcription factors in regulation of the murine CTP:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase alpha promoter.J Lipid Res. 2000 Apr;41(4):583-94. J Lipid Res. 2000. PMID: 10744779
-
Sp1 and Sp3 transcription factors synergistically regulate HGF receptor gene expression in kidney.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003 Jan;284(1):F82-94. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00200.2002. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12473536
-
Enhanced binding of Sp1/Sp3 transcription factors mediates the hyperoxia-induced increased expression of the lung type I cell gene T1alpha.J Cell Biochem. 2003 Aug 1;89(5):887-901. doi: 10.1002/jcb.10555. J Cell Biochem. 2003. PMID: 12874823
-
Gene regulation by Sp1 and Sp3.Biochem Cell Biol. 2004 Aug;82(4):460-71. doi: 10.1139/o04-045. Biochem Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15284899 Review.
Cited by
-
MIWE: detecting the critical states of complex biological systems by the mutual information weighted entropy.BMC Bioinformatics. 2024 Jan 27;25(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s12859-024-05667-z. BMC Bioinformatics. 2024. PMID: 38280998 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering uncharacterized binding of transcription factors from ATAC-seq footprinting data.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 23;14(1):9275. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-59989-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38654130 Free PMC article.
-
Single-nucleus multi-omics of Parkinson's disease reveals a glutamatergic neuronal subtype susceptible to gene dysregulation via alteration of transcriptional networks.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2024 Jul 2;12(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s40478-024-01803-1. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2024. PMID: 38956662 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blondel, V. D., Guillaume, J.-L., Lambiotte, R. and Lefebvre, E. (2008). Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. "J. Stat. Mech., Theory Exp." 2008, P10008. 10.1088/1742-5468/2008/10/P10008 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

