Mixed Origins: HIV gp120-Specific Memory Develops from Pre-Existing Memory and Naive B Cells Following Vaccination in Humans
- PMID: 36762930
- PMCID: PMC10398743
- DOI: 10.1089/AID.2022.0104
Mixed Origins: HIV gp120-Specific Memory Develops from Pre-Existing Memory and Naive B Cells Following Vaccination in Humans
Abstract
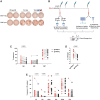
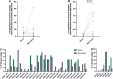
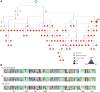
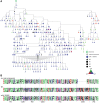
The most potent and broad HIV envelope (Env)-specific antibodies often when reverted to their inferred germline versions representing the naive B cell receptor, fail to bind Env, suggesting that the initial responding B cell population not only exclusively comprises a naive population, but also a pre-existing cross-reactive antigen-experienced B cell pool that expands following Env exposure. Previously we isolated gp120-reactive monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) from participants in HVTN 105, an HIV vaccine trial. Using deep sequencing, focused on immunoglobulin G (IgG), IgA, and IgM, VH-lineage tracking, we identified four of these mAb lineages in pre-immune peripheral blood. We also looked through the ∼7 month postvaccination bone marrow, and interestingly, several of these lineages that were found in prevaccination blood were still persistent in the postvaccination bone marrow, including the CD138+ long-lived plasma cell compartment. The majority of the pre-immune lineage members included IgM, however, IgG and IgA members were also prevalent and exhibited somatic hypermutation. These results suggest that vaccine-induced gp120-specific antibody lineages originate from both naive and cross-reactive memory B cells. ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02207920.
Keywords: B cell; HIV-1; antibody repertoire; envelope; gp120; memory; naive; pre-immune.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

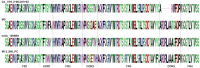
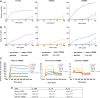
Similar articles
-
HIV-1 gp120 vaccine induces affinity maturation in both new and persistent antibody clonal lineages.J Virol. 2012 Jul;86(14):7496-507. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00426-12. Epub 2012 May 2. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22553329 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Antibody Responses to the V1V2 and V3 Regions of HIV-1 Envelope by Immune Complex Vaccines.Front Immunol. 2018 Oct 26;9:2441. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02441. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30416503 Free PMC article.
-
Combined HIV-1 Envelope Systemic and Mucosal Immunization of Lactating Rhesus Monkeys Induces a Robust Immunoglobulin A Isotype B Cell Response in Breast Milk.J Virol. 2016 Apr 29;90(10):4951-4965. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00335-16. Print 2016 May 15. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 26937027 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Features of Broadly Neutralizing Antibodies and Rational Design of Vaccine.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1075:73-95. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-0484-2_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30030790 Review.
-
Strategies for induction of HIV-1 envelope-reactive broadly neutralizing antibodies.J Int AIDS Soc. 2021 Nov;24 Suppl 7(Suppl 7):e25831. doi: 10.1002/jia2.25831. J Int AIDS Soc. 2021. PMID: 34806332 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring HIV Vaccine Progress in the Pre-Clinical and Clinical Setting: From History to Future Prospects.Viruses. 2024 Feb 27;16(3):368. doi: 10.3390/v16030368. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38543734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Highly Cross-Reactive and Protective Influenza A Virus H3N2 Hemagglutinin- and Neuraminidase-Specific Human Monoclonal Antibodies.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Aug 17;11(4):e0472822. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.04728-22. Epub 2023 Jun 15. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37318331 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. WHO HIV/AIDS Data and Statistics. 2019. Available from: https://www.who.int/hiv/data/en [Last accessed: June 30, 2022].
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

